Dizziness In Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Practice: History And Physical Examination Page 24
ADVERTISEMENT
tal SCC
. Nystagmus will occur in both directions
Walk-Rotate-Walk Test
41
but will generally be stronger with the head turned
In this test for the horizontal SCC
, the patient
117
towards the affected side
.
41
walks straight ahead at the patient-selected maximum
Positional nystagmus on this test has been shown
tolerable speed in a room with ample space. The patient
to identify patients with posterior SCC BPPV with
then rotates 180
on the axis of the rotation direction
0
78% sensitivity
. Sensitivity as high as 88% has been
116
foot, returning back in a continuous movement. The
reported
.
69
test is performed to both sides. Staggering, sidestepping;
making corrective movements of the body or hands,
Straight Head-Hanging Test
discontinuing the rotation in one direction, or slowed
In the straight head-hanging test, the patient is
difficult rotation indicate a positive test. A positive
assisted in lying back from long sitting with the head
response on rotation right implicates the right and a
extended but not rotated. This test may be more sensitive
positive response on rotation left implicates the left SCC.
for anterior SCC BPPV: An additional 20
of extension
0
The difference must persist over 3 repetitions. Rahko
as compared to the Hallpike-Dix maneuver causes the
and Kotti
found 100% predictive validity for this test
117
ampullary segment of the anterior SCC to approach a
in determining a positive response to a horizontal SCC
more vertical position
. We found no data on reliability
76
BPPV treatment. The 180
turn in this versus the 90
0
0
and validity.
turn in the roll test may allow for higher otoconia ac-
celeration and ampulla cell stimulation. Sensitivity was
Roll Test
acceptable; some patients with acute vestibular neuritis
The roll test detects horizontal SCC BPPV
. The
115
tested positive on the walk-rotate-walk test
.
117
therapist quickly “logrolls” the supine patient with the
head 30
flexed to one side maintaining this position for
0
Cervicogenic Dizziness Testing
≥1 minute. Otoconia moving back and forth within the
SCC with left and right rotation will cause the positive
The neck torsion test (Figures 8A & B) is used to
response of nystagmus and vertigo
. Canalithiasis causes
115
detect cervicogenic dizziness
. The head is held
118,119
fatiguing geotropic (towards the earth) nystagmus and
stationary during neck and trunk rotation. An alternate
cupulolithiasis persistent apogeotropic (away from the
way of screening the cervical spine as the possible origin
earth) nystagmus
. More severe and longer lasting
115
of dizziness symptoms is to have the patient sit and flex
symptoms indicate the affected side
. We found no data
115
forward at the hips simultaneously extending and rotat-
on reliability and validity.
ing their neck (Figure 9)
. As both tests keep the inner
120
Fig. 8a-b: Neck torsion test
Dizziness in Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Practice:
History and Physical Examination / 245
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22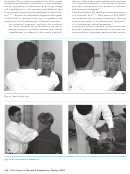 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30








