The Great War - History Book Chapter Page 12
ADVERTISEMENT
invading Russian army and drove it into full retreat. More
than 30,000 Russian soldiers were killed.
Russia fared somewhat better against the Austrians.
Russian forces defeated the Austrians twice in September
1914, driving deep into their country. Not until December
of that year did the Austrian army manage to turn the tide.
Austria defeated the Russians and eventually pushed them
out of Austria-Hungary.
Russia Struggles
By 1916, Russia’s war effort was near
collapse. Unlike the nations of western Europe, Russia had
yet to become industrialized. As a result, the Russian army
was continually short on food, guns, ammunition, clothes,
The Frozen Front
boots, and blankets. Moreover, the Allied supply shipments
For soldiers on the Eastern Front, like
to Russia were sharply limited by German control of the
those shown above, the overall misery
Baltic Sea, combined with Germany’s relentless submarine
of warfare was compounded by deadly
campaign in the North Sea and beyond. In the south, the
winters. “Every day hundreds froze to
Ottomans still controlled the straits leading from the
death,” noted one Austro-Hungarian
Mediterranean to the Black Sea.
officer during a particularly brutal spell.
The Russian army had only one asset—its numbers.
Russian troops suffered too, mainly
due to their lack of food and clothing.
Throughout the war the Russian army suffered a stagger-
“I am at my post all the time—frozen
ing number of battlefield losses. Yet the army continually
[and] soaked . . . ,” lamented one
rebuilt its ranks from the country’s enormous population.
soldier. “We walk barefoot or in rope-
For more than three years, the battered Russian army man-
soled shoes. It’s incredible that soldiers
aged to tie up hundreds of thousands of German troops
of the Russian army are in rope-
in the east. As a result, Germany could not hurl its full
soled shoes!”
Synthesizing
fighting force at the west.
Why was
Russia’s involve-
Germany and her allies, however, were concerned with
ment in the war so
more than just the Eastern or Western Front. As the war raged on, fighting spread
important to the
beyond Europe to Africa, as well as to Southwest and Southeast Asia. In the years after
other Allies?
it began, the massive European conflict indeed became a world war.
2
SECTION
ASSESSMENT
TERMS & NAMES
For each term or name, write a sentence explaining its significance.
1.
•
Central Powers
•
Allies
•
Western Front
•
Schlieffen Plan
•
trench warfare
•
Eastern Front
USING YOUR NOTES
MAIN IDEAS
CRITICAL THINKING & WRITING
What were some of the
Which countries comprised the
How was war on the
2.
3.
6. COMPARING AND CONTRASTING
conditions that soldiers on the
Central Powers? Which
Western and Eastern Fronts different? How was it the
front lines had to face?
countries comprised the Allies?
same?
4.
What were the characteristics
7. ANALYZING CAUSES
Why did the Schlieffen Plan
of trench warfare?
ultimately collapse? Cite specific details from the text.
I. The Great War
Begins
What factors contributed to
Why might it be fair to say that
5.
8. MAKING INFERENCES
A.
Russia’s war difficulties?
neither side won the battles of the Somme or Verdun?
B.
In an
9. WRITING ACTIVITY
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
II. A Bloody Stalemate
explanatory essay, describe the effects of the new
technology on warfare. Use examples from your reading.
CONNECT TO TODAY
PRESENTING AN ORAL REPORT
Find an image of a World War I monument from any one of the combatant countries. In an
oral report, present the image to the class and provide details about its origin and purpose.
849
The Great War
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1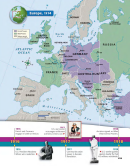 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26