The Great War - History Book Chapter Page 18
ADVERTISEMENT
Allied View of Armistice
German Reaction to Armistice
News of the armistice affected the Allied and Central
On the other side of the fighting line, German officer
powers differently. Here, a U.S. soldier named Harry
Herbert Sulzbach struggled to inform his troops of the
Truman, who would go on to become president, recalls
war’s end.
the day the fighting stopped.
P R I M A R Y S O U R C E
P R I M A R Y S O U R C E
Every single one of them [the French soldiers] had to
“Hostilities will cease as from 12 noon today. ” This was
march by my bed and salute and yell, “Vive President
the order which I had to read out to my men. The war
Wilson, Vive le capitaine d’artillerie américaine!” No
is over. . . . How we looked forward to this moment;
sleep all night. The infantry fired Very pistols, sent up
how we used to picture it as the most splendid event
all the flares they could lay their hands on, fired rifles,
of our lives; and here we are now, humbled, our souls
pistols, whatever else would make noise, all night long.
torn and bleeding, and know that we’ve surrendered.
Germany has surrendered to the Entente!
HARRY TRUMAN, quoted in The First World War
HERBERT SULZBACH, With the German Guns
DOCUMENT-BASED QUESTIONS
1.
Summarizing What is the main difference between these two excerpts?
2.
Drawing Conclusions How did Herbert Sulzbach’s vision of the armistice differ from
what actually occurred?
The Central Powers Collapse
Russia’s withdrawal from the war at last allowed
Germany to send nearly all its forces to the Western Front. In March 1918, the
Germans mounted one final, massive attack on the Allies in France. As in the open-
ing weeks of the war, the German forces crushed everything in their path. By late
May 1918, the Germans had again reached the Marne River. Paris was less than 40
miles away. Victory seemed within reach.
By this time, however, the German military had weakened. The effort to reach
the Marne had exhausted men and supplies alike. Sensing this weakness, the
Allies—with the aid of nearly 140,000 fresh U.S. troops—launched a counterat-
tack. In July 1918, the Allies and Germans clashed at the Second Battle of the
Marne. Leading the Allied attack were some 350 tanks that rumbled slowly for-
ward, smashing through the German lines. With the arrival of 2 million more
Comparing
American troops, the Allied forces began to advance steadily toward Germany.
How was the
Second Battle of
Soon, the Central Powers began to crumble. First the Bulgarians and then the
the Marne similar
Ottoman Turks surrendered. In October, revolution swept through Austria-
to the first?
Hungary. In Germany, soldiers mutinied, and the public turned on the kaiser.
On November 9, 1918, Kaiser Wilhelm II stepped down. Germany declared itself
a republic. A representative of the new German government met with French
armistice
Commander Marshal Foch in a railway car near Paris. The two signed an
,
or an agreement to stop fighting. On November 11, World War I came to an end.
The Legacy of the War
World War I was, in many ways, a new kind of war. It involved the use of new
technologies. It ushered in the notion of war on a grand and global scale. It also
left behind a landscape of death and destruction such as was never before seen.
Both sides in World War I paid a tremendous price in terms of human life.
About 8.5 million soldiers died as a result of the war. Another 21 million were
wounded. In addition, the war led to the death of countless civilians by way of
855
The Great War
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1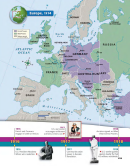 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22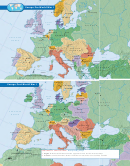 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26