The Great War - History Book Chapter Page 22
ADVERTISEMENT
between Germany and the Allied powers was
signed on June 28, 1919, five years to the day
after Franz Ferdinand’s assassination in Sarajevo.
Woodrow Wilson
Adopting Wilson’s fourteenth point, the treaty
1856–1924
created a
League of Nations
. The league was to
Wilson was tall and thin and
be an international association whose goal would
often in poor health. He
be to keep peace among nations.
suffered from terrible
The treaty also punished Germany. The
indigestion and sometimes
defeated nation lost substantial territory and had
had to use a stomach pump
on himself. A scholarly man,
severe restrictions placed on its military opera-
Wilson once served as
tions. As tough as these provisions were, the
president of Princeton
harshest was Article 231. It was also known as the
University in New Jersey.
“war guilt” clause. It placed sole responsibility
Passionate about
for the war on Germany’s shoulders. As a result,
international peace, he took on the U.S. Senate
Vocabulary
Germany had to pay reparations to the Allies.
after it vowed to reject the Treaty of Versailles.
Reparations is
money paid by a
During the political battle, he suffered a stroke
All of Germany’s territories in Africa and the
defeated nation to
that disabled him for the rest of his term.
Pacific were declared mandates, or territories to
compensate for
be administered by the League of Nations.
Georges Clemenceau
damage or injury
1841–1929
Under the peace agreement, the Allies would
during a war.
The near opposite of Wilson,
govern the mandates until they were judged
Clemenceau had a compact
ready for independence.
physique and a combative
style that earned him the
A Troubled Treaty
nickname “Tiger.” He had
worked as a physician and
The Versailles treaty was just one of five treaties
journalist before entering
negotiated by the Allies. In the end, these agree-
the political arena.
ments created feelings of bitterness and
Determined to punish
betrayal—among the victors and the defeated.
Germany, Clemenceau rarely
agreed with Wilson and his larger quest for
The Creation of New Nations
The Western
world peace. He once remarked of Wilson, “He
powers signed separate peace treaties in 1919 and
thinks he is another Jesus Christ come upon
1920 with each of the other defeated nations:
earth to reform men. ”
Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman
Empire. These treaties, too, led to huge land losses
For more on Woodrow
RESEARCH LINKS
for the Central Powers. Several new countries were
Wilson and Georges Clemenceau, go to
created out of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia
were all recognized as independent nations.
The Ottoman Turks were forced to give up almost all of their former empire.
They retained only the territory that is today the country of Turkey. The Allies
carved up the lands that the Ottomans lost in Southwest Asia into mandates rather
than independent nations. Palestine, Iraq, and Transjordan came under British con-
trol; Syria and Lebanon went to France.
Russia, which had left the war early, suffered land losses as well. Romania and
Poland both gained Russian territory. Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, for-
merly part of Russia, became independent nations.
“A Peace Built on Quicksand”
In the end, the Treaty of Versailles did little to
build a lasting peace. For one thing, the United States—considered after the war to
be the dominant nation in the world—ultimately rejected the treaty. Many
Americans objected to the settlement and especially to President Wilson’s League
of Nations. Americans believed that the United States’ best hope for peace was to
stay out of European affairs. The United States worked out a separate treaty with
Germany and its allies several years later.
859
The Great War
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1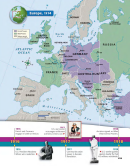 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22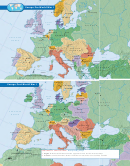 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26