Instructions For California Withholding Schedules - Method B - Exact Calculation Method - 2001 Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
CALIFORNIA WITHHOLDING SCHEDULES FOR 2001
METHOD B - EXACT CALCULATION METHOD
This method is based upon applying a given percentage to the wages (after deductions) which fall within a taxable income class,
adding to this product the accumulated tax for all lower tax brackets, and then subtracting a tax credit based upon the number of
allowances claimed on the Employee's Withholding Allowance Certificate (EDD form DE 4 or Federal Form W-4). This method also
takes into consideration the special treatment of additional allowances for estimated deductions.
The steps in computing the amount of tax to be withheld are as follows:
Step 1
Determine if the employee's gross salaries and wages are LESS than, or equal to, the amount shown in “TABLE 1
- LOW INCOME EXEMPTION TABLE.” If so, no income tax is required to be withheld.
Step 2
If the employee claims any additional withholding allowances for estimated deductions from form DE 4, subtract
the amount shown in “TABLE 2 - ESTIMATED DEDUCTION TABLE” from the gross salaries and wages.
Step 3
Subtract the standard deduction amount shown in “TABLE 3 - STANDARD DEDUCTION TABLE” to arrive at the
employee's taxable income.
Step 4
Use "TABLE 5 - TAX RATE TABLE” for the payroll period and marital status to find the applicable line on which
the taxable income is located. Perform the indicated calculations to arrive at the computed tax liability.
Step 5
Subtract the tax credit shown in “TABLE 4 – EXEMPTION ALLOWANCE TABLE”* from the computed tax liability
to arrive at the amount of tax to be withheld.
*
If the employee uses additional allowances claimed for estimated deductions, such allowances MUST NOT be used in
the determination of tax credits to be subtracted.
EXAMPLE A:
Weekly earnings of $160.00, single, and claiming one withholding allowance on form DE 4 or W-4.
Step 1
Earnings for the weekly payroll period are LESS than the amount shown in "TABLE 1 - LOW INCOME
EXEMPTION TABLE" ($179.00); therefore, no income tax is to be withheld.
EXAMPLE B:
Biweekly earnings of $950.00, married, and claiming three withholding allowances, one of which is for estimated
deductions.
Step 1
Earnings for the biweekly payroll period are GREATER than the amount shown in "TABLE 1 - LOW INCOME
EXEMPTION TABLE" ($715.00); therefore, income tax should be withheld.
Step 2
Earnings for biweekly payroll period......................................................................................
$950.00
Subtract amount from "TABLE 2 - ESTIMATED DEDUCTION TABLE"................................
-38.00
Salaries and wages subject to withholding............................................................................
$912.00
Step 3
Subtract amount from "TABLE 3 - STANDARD DEDUCTION TABLE".................................
-216.00
Taxable income .....................................................................................................................
$696.00
Step 4
Tax computation from "TABLE 5 - TAX RATE TABLE":
Entry covering $696.00 (over $420 but not over $996)
•
2% of amount over $420.00 (.02 x [$696 – 420]) ...........................................................
$
5.52
•
Plus the marginal amount...............................................................................................
+4.20
•
Computed tax.................................................................................................................
9.72
Step 5
Subtract amount from "TABLE 4 – EXEMPTION ALLOWANCE TABLE" for
2 regular withholding allowances.........................................................................................
-5.77
Net amount of tax to be withheld ...........................................................................................
$
3.95
======
NOTE: Table 5 provides a method comparable to the federal alternative method for percentage calculation of
withholding. This method is a minor simplification of the exact calculation method described above in that
the tax rate applies to the total taxable income with the excess amount subtracted.
Method B (INTERNET)
Page 2 of 10
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4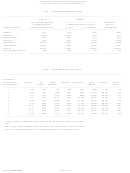 5
5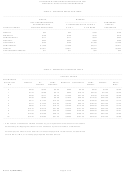 6
6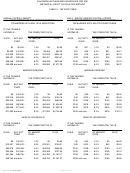 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10








