Buffer Solutions Worksheets
ADVERTISEMENT
Worksheet 24 - Buffers
A buffer solution is one which maintains an approximately constant pH when
small amounts of either a strong acid or base are added. Solutions containing
either weak acids and their conjugate bases, or weak bases and their conjugate
acids, can be buffering solutions.
1. The number of moles of the conjugate pairs must be large compared to the
moles of added strong acids or bases.
2. The ratio of the conjugate pair ([weak acid]/[conjugate base] or [weak base] /
[conjugate acid]) should lie between 0.1 and 10, with optimal buffering at a 1:1
ratio.
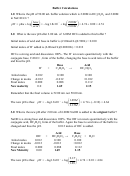
3. The pH of a 1:1 ratio buffer is equal to the pK
of the weak acid or pK
of the
a
b
weak base. The effective range is ± 1 from the pK
or pK
.
a
b
-
-5
CH
COOH/CH
COO
K
= 1.8 x 10
3
3
a
+
-5
NH
/NH
K
= 1.8 x 10
3
4
b
-
2-
-11
HCO
/CO
K
= 5.6 x 10
3
3
a
-
2-
-8
H
PO
/HPO
K
= 6.2 x 10
2
4
4
a
1.
Which of the conjugate pairs, shown above would be appropriate for
preparing a buffer at pH = 7.0?
2.
What is the pH of a buffer formed from 50 mL of 15.0 M NH
and 53.5 g of
3
NH
Cl in enough water to make 500 mL of solution?
4
3.
What is the pH of the previous solution after addition of 100 mL of 0.2 M
NaOH?
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2