Print
Clear
501
Page 7
Georgia Form
NEW INFORMATION
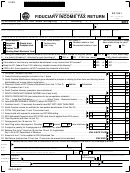
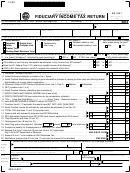
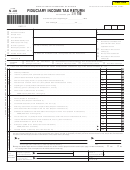
Fiduciary Income Tax Return
Federal Tax Changes
The Governor signed House Bill 292 into law. Consequently, for
• 5 year carryback of NOLs incurred in the Kansas disaster area after
taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2015, with exceptions
May 3, 2007, I.R.C. Section 1400N(k).
discussed below, Georgia has adopted the provisions of all federal
• 5 year carryback of certain disaster losses, I.R.C. Sections
acts (as they relate to the computation of federal adjusted gross
172(b)(1)(J) and 172(j).
income (AGI) for individuals or federal taxable income for non -
• The election to deduct public utility property losses attributable to
individuals) that were enacted on or before January 1, 2015. For
May 4, 2007 Kansas storms and tornadoes in the fifth tax year before
2015, for Georgia purposes, the I.R.C. Section 179 deduction is
the year of the loss, I.R.C. Section 1400N(o).
limited to $25,000 and the related phase out is 200,000. Georgia
• Special rules relating to a financial institution being able to use
has not adopted the Section 179 deduction for certain real property.
ordinary gain or loss treatment for the sale or exchange of certain
preferred stock after Dec. 31, 2007, I.R.C. Section 1221.
• Temporary tax relief provisions relating to the Midwestern disaster
Exceptions
area, I.R.C. Sections 1400N(f) and 1400N(k).
Georgia has Not adopted I.R.C. Section 168(k) (the 30%, 50% and
100% bonus depreciation rules) except for I.R.C. Section
Depreciation Differences. Depreciation differences due to the Fed-
168(k)(2)(A)(i) (the definition of qualified property), I.R.C. Section
eral acts mentioned above should be treated as follows (If the tax-
168(k)(2)(D)(i) (exceptions to the definition of qualified property), and
payer has depreciation differences from more than one Federal act,
I.R.C. Section 168(k)(2)(E) (special rules for qualified property) and
it is not necessary to make a separate adjustment for each act):
Georgia has not adopted I.R.C. Section 199 (federal deduction for
A. Depreciation must be computed one way for Federal purposes
income attributable to domestic production activities).
and another way for Georgia purposes. To compute depreciation for
Georgia has also not adopted the following:
Federal purposes, taxpayers should use the current year IRS Form
• The exclusion of $2,400 of unemployment income for 2009, I.R.C.
4562 and attach it to the Georgia return. This should be entered on
Section 85(c).
the other addition line of the return.
• Additional itemized deduction for the sales tax on the purchase of a
B. Depreciation must also be computed for Georgia purposes.
new vehicle in 2009, I.R.C. Sections 164(a)(6) and 164(b)(6). Please
Taxpayers should use Georgia Form 4562 to compute depreciation
note: Georgia also does not allow the increased standard deduction
for Georgia purposes and attach it to the Georgia return. This should
for sales tax on the purchase of a new vehicle in 2009 because
be entered on the other subtraction line of the return.
Georgia has its own standard deduction.
• The election to increase the normal two year net operating loss
Federal deduction for income attributable to domestic production
carryback to 3, 4, or 5 years for tax years 2008 and 2009, I.R.C.
activities (IRC Section 199). This adjustment should be entered on
Sections 172(b)(1)(H) and 810(b)(4).
the addition line of the applicable return. An adjustment to the Geor-
• The transition rule that would allow a taxpayer to revoke a prior
gia partnership or S Corporation return is not required if the partner-
election to forego the net operating loss carryback period.
ship or S Corporation is not allowed the Section 199 deduction di-
• Deferral of debt income from reacquisitions of business debt at a
rectly, but instead passes through the information, needed to com-
discount in 2009 and 2010; federally deferred for up to five years,
pute the deduction, to the partners or shareholders.
then included ratably over five years, I.R.C. Section 108(i).
• Modified rules for high yield original issue discount obligations,
Other Differences. Other differences should be placed on the other
I.R.C. Sections 163(e)(5)(F) and 163(i)(1).
addition or subtraction line of the applicable return. Attach a state-
• New York Liberty Zone Benefits, I.R.C. Section 1400L.
ment to the return explaining these differences.
• 50% first year depreciation for post 8/28/2006 Gulf Opportunity Zone
Additionally, the provisions listed above may have an indirect effect
property, I.R.C. Section 1400N(d)(1).
on the calculation of Georgia taxable income.
• 50% bonus depreciation for most tangible property and computer
Adjustments for the items listed below should be added or sub-
software bought after May 4, 2007 and placed in service in the Kan-
tracted on your Georgia income tax form.
sas Disaster Area, I.R.C. Section 1400N(d)(1).
1. When property is sold for which the bonus depreciation was
• 50% bonus depreciation for “qualified reuse and recycling prop-
claimed, there will be a difference in the gain or loss on the sale of
erty,” I.R.C. Section 168(m).
the property.
• 50% bonus depreciation in connection with disasters federally de-
2. The depreciation adjustment may be different if the taxpayer is
clared after 2007, I.R.C. Section 168(n).
subject to the passive loss rules and is not able to claim the addi-
• Increased ($8,000) first-year depreciation limit for passenger auto-
tional depreciation on the Federal return.
mobiles if the passenger automobile is “qualified property,” I.R.C.
3. Other Federal items that are computed based on federal adjusted
Section 168(k).
gross income or federal taxable income will have to be recomputed
• 15 year straight-line cost recovery period for certain improvements
if the provisions of the Federal Acts are claimed.
to retail space, I.R.C. Sections 168(e)(3)(E)(ix), 168(e)(8), and
168(b)(3)(I).
Furthermore, in 2003 the IRS started requiring separate reporting, to
• Modified rules relating to the 15 year straight-line cost recovery for
shareholders of S Corporations and partners of partnerships, for
qualified restaurant property (allowing buildings to now be included),
the gain from asset sales for which an I.R.C. Section 179 deduction
I.R.C. Section 168(e)(7).
was claimed. Georgia follows the separate reporting treatment of
•5 year depreciation life for most new farming machinery and equip-
the gain and the Section 179 deduction. Accordingly, the gain should
ment, I.R.C. Section 168(e)(3)(B)(vii).
not be reported directly on the S Corporation or partnership return,
• Special rules relating to Gulf Opportunity Zone public utility casualty
but the gain, along with any Georgia adjustment to the gain (due to
losses, I.R.C. Section 1400N(j).
the Federal acts), should be reported separately to the sharehold-
•5 year carryback of NOLs attributable to Gulf Opportunity Zone losses,
ers or partners.
I.R.C. Section 1400N(k).
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9