Factoring Worksheet With Examples Page 31
ADVERTISEMENT
The Algebra Lab leads to the following rule for finding the difference of
two squares.
Difference of Squares
2
2
Symbols
a
- b
= (a + b)(a - b) or (a - b)(a + b)
2
x
- 9 = (x + 3)(x - 3) or (x - 3)(x + 3)
Examples
EXAMPLE
Factor the Difference of Squares
Factor each binomial.
2
a. n
- 25
2
2
2
2
2
n
- 25 = n
- 5
Write in the form a
- b
.
= (n + 5)(n - 5)
Factor the difference of squares.
2
2
b. 36 x
- 49 y
2
2
2
2
2
2
36 x
- 49 y
= (6x)
- (7y)
36x
= 6x · 6x and 49y
= 7y · 7y
= (6x + 7y)(6x - 7y)
Factor the difference of squares.
3
c. 48 a
- 12a
If the terms of a binomial have a common factor, the GCF should be
factored out first before trying to apply any other factoring technique.
3
2
3
- 12a = 12a(4 a
- 1)
48 a
The GCF of 48 a
and -12a is 12a.
2
2
= 12a[ (2a) - 1
]
4 a
= 2a · 2a and 1 = 1 · 1
= 12a(2a + 1)(2a - 1)
Factor the difference of squares.
2
2
2
1
A.
81 - t
1
B.
64 g
- h
3
3
1
1
C.
9 x
- 4x
D.
-4 y
+ 9y
Occasionally, the difference of squares pattern needs to be applied more than
once to factor a polynomial completely.
EXAMPLE
Apply a Factoring Technique More Than Once
4
Factor x
- 81.
2
Common
4
2
2
4
2
2
x
- 81 = [ ( x
)
- 9
]
x
= x
· x
and 81 = 9 · 9
Misconception
2
2
= ( x
+ 9)( x
- 9)
Factor the difference of squares.
Remember that the
sum of two squares,
2
2
2
2
= ( x
+ 9)( x
- 3
)
x
= x · x and 9 = 3 · 3
2
2
x
+ a
, is not
2
2
2
factorable. x
+ a
is
= ( x
+ 9)(x + 3)(x - 3)
Factor the difference of squares.
a prime polynomial.
Factor each binomial.
4
4
4
2
A.
y
- 1
2
B.
4 a
- 4 b
448
Extra Examples at
Chapter 8 Factoring
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7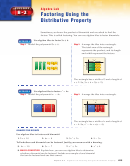 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24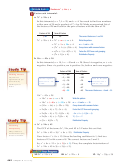 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50