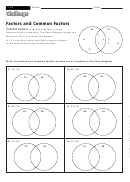
Factoring Worksheet With Examples Page 40
ADVERTISEMENT
2
You have solved equations like x
- 36 = 0 by factoring. You can also use the
definition of a square root to solve this equation.
Reading Math
2
x
- 36 = 0
Original equation
Square Root
2
x
= 36
Add 36 to each side.
√
Solutions ±
36 is
x = ± √ 36
Take the square root of each side.
read as plus or minus
the square root of 36.
Remember that there are two square roots of 36, namely 6 and -6. Therefore,
the solution set is {-6, 6}. You can express this as {±6}.
Square Root Property
2
For any number n > 0, if x
= n, then x = ±
n .
Symbols
√
2
x
= 9
Example
x = ± √ 9 or ±3
EXAMPLE
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
During an experiment, a ball is dropped from a height
2
of 205 feet. The formula h = -16 t
+ h
can be used to approximate the
0
number of seconds t it takes for the ball to reach height h from an initial
height h
in feet. Find the time it takes the ball to reach the ground.
0
2
h = -16 t
+ h
Original formula
0
2
0 = -16 t
+ 205
Replace h with 0 and h
with 205.
0
2
-205 = -16 t
Subtract 205 from each side.
2
12.8125 = t
Divide each side by -16.
±3.6 ≈ t
Take the square root of each side.
Since a negative number does not make sense in this situation, the
solution is 3.6. This means that it takes about 3.6 seconds for the ball
to reach the ground.
4
.
Find the time it takes a ball to reach the ground if it is dropped from a
bridge that is half as high as the one described above.
EXAMPLE
Use the Square Root Property to Solve Equations
Solve each equation. Check the solutions.
2
a. (a + 4 )
= 49
2
(a + 4 )
= 49
Original equation
a + 4 = ± √ 49
Square Root Property
a + 4 = ±7
49 = 7 · 7
a = -4 ± 7
Subtract 4 from each side.
a = -4 + 7 or a = -4 - 7
Separate into two equations.
= 3
= -11
Simplify.
The roots are
11 and 3.
Check in the original equation.
(continued on the next page)
457
Extra Examples at
Lesson 8-6 Perfect Squares and Factoring
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50