Factoring Worksheet With Examples Page 44
ADVERTISEMENT
Study Guide
Download Vocabulary
8
Review from
and Review
Key Vocabulary
composite number
perfect square trinomials
(p. 420)
Be sure the following
(p. 454)
factored form
(p. 421)
Key Concepts are noted
prime factorization
(p. 421)
in your Foldable.
factoring
(p. 426)
prime number
(p. 420)
factoring by grouping
prime polynomial
(p. 427)
(p. 443)
Key Concepts
greatest common factor
roots
(p. 428)
Monomials and Factoring
(Lesson 8-1)
(p. 422)
• The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or
more monomials is the product of their common
prime factors.
Vocabulary Check
Factoring Using the Distributive Property
State whether each sentence is true or false.
(Lesson 8-2)
• Using the Distributive Property to factor
If false, replace the underlined word,
phrase, expression, or number to make
polynomials with four or more terms is called
factoring by grouping.
a true sentence.
ax + bx + ay + by = x(a + b) + y(a + b)
1. The number 27 is an example of a prime
= (a + b)(x + y)
number.
2
2. 2x is the greatest common factor of 12 x
• Factoring can be used to solve some equations.
According to the Zero Product Property, for any
and 14xy.
real numbers a and b, if ab = 0, then either
3. 66 is an example of a perfect square.
a = 0, b = 0, or both a and b equal zero.
4. 61 is a factor of 183.
Factoring Trinomials and Differences
2
5. The prime factorization of 48 is 3 · 4
.
of Squares
(Lessons 8-3, 8-4, and 8-5)
2
6. x
- 25 is an example of a perfect square
2
• To factor x
+ bx + c, find m and n with a
trinomial.
sum of b and a product of c. Then write
7. The number 35 is an example of a
2
x
+ bx + c as (x + m)(x + n).
composite number.
2
• To factor a x
+ bx + c, find m and n with a
2
8. x
- 3x - 70 is an example of a prime
product of ac and a sum of b. Then write as
polynomial.
2
ax
+ mx + nx + c and factor by grouping.
9. Expressions with four or more unlike
2
2
a
- b
= (a + b)(a - b) or (a - b)(a + b)
terms can sometimes be factored by
grouping.
Perfect Squares and Factoring
(Lesson 8-6)
2
2
2
• a
+ 2ab + b
= (a + b )
and
10. (b - 7)(b + 7) is the factorization of a
2
2
2
a
- 2ab + b
= (a - b )
difference of squares.
• For a trinomial to be a perfect square, the first and
last terms must be perfect squares, and the middle
term must be twice the product of the square
roots of the first and last terms.
2
• For any number n > 0, if x
= n, then x = ±
n .
√
Vocabulary Review at
461
Chapter 8 Study Guide and Review
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7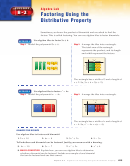 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50