Factoring Worksheet With Examples Page 39
ADVERTISEMENT
EXAMPLE
Factor Completely
Factor each polynomial.
2
Factoring
a. 4 x
- 36
Methods
First check for a GCF. Then, since the polynomial has two terms, check for
When there is a GCF
the difference of squares.
other than 1, it is
usually easier to factor
2
2
4 x
- 36 = 4( x
- 9)
4 is the GCF.
it out first. Then, check
2
2
2
the appropriate
= 4( x
- 3
)
x
= x · x and 9 = 3 · 3
factoring methods in
= 4(x + 3)(x - 3)
Factor the difference of squares.
the order shown in the
table.
2
b. 25 x
+ 5x - 6
2
+ bx + c. Are
This is not a perfect square trinomial. It is of the form a x
there two numbers m and n with a product of 25(-6) or -150 and a sum
of 5? Yes, the product of 15 and -10 is -150 and the sum is 5.
2
2
+ 5x - 6 = 25 x
+ mx + nx - 6
25 x
Write the pattern.
2
= 25 x
+ 15x - 10x - 6
m = 15 and n = -10
2
= (25 x
+ 15x) + (-10x - 6)
Group terms with common factors.
= 5x(5x + 3) - 2(5x + 3)
Factor out the GCF from each grouping.
= (5x + 3)(5x - 2)
5x + 3 is the common factor.
2
2
2
2
A.
2 x
- 32
B.
9 t
- 3t - 20
Personal Tutor at
Solve Equations with Perfect Squares
When solving equations involving
repeated factors, it is only necessary to set one of the repeated factors equal
to zero.
EXAMPLE
Solve Equations with Repeated Factors
_
1
2
- x +
= 0.
Solve x
4
_
1
2
x
- x +
= 0
Original equation
4
2
(
_
)
(
_
)
1
1
_
1
2
2
x
- 2(x)
+
= 0
Recognize x
- x +
as a perfect square trinomial.
4
2
2
2
_
(
)
1
x -
= 0
Factor the perfect square trinomial.
2
_
1
x -
= 0
Set repeated factor equal to zero.
2
_
1
x =
Solve for x.
2
Solve each equation. Check the solutions.
_
_
4
4
2
2
3
A.
a
+ 12a + 36 = 0
3
B.
y
-
y +
= 0
3
9
456
Chapter 8 Factoring
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24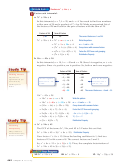 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50