Redox And Electrochemistry Worksheet With Answer Key Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
half–reaction occurs at each electrode.
(d) Select two of the gases obtained in these experiments, and for each gas, indicate one
experimental procedure that can be used to identify it.
#3
An electrochemical cell consists of a tin electrode in an acidic solution of 1.00 molar
2+
Sn
connected by a salt bridge to a second compartment with a silver electrode in an
+
acidic solution of 1.00 molar Ag
.
(a) Write the equation for the half–cell reaction occurring at each electrode. Indicate
which half–reaction occurs at the anode.
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall spontaneous cell reaction that
occurs when the circuit is complete. Calculate the standard voltage, E˚, for this cell
reaction.
(c) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this cell reaction at 298K.
(d) A cell similar to the one described above is constructed with solutions that have
2+
+
initial concentrations of 1.00 molar Sn
and 0.0200 molar Ag
. Calculate the initial
voltage, E˚, of this cell.
#4
The electrolysis of an aqueous solution of potassium iodide, KI, results in the formation
of hydrogen gas at the cathode and iodine at the anode. A sample of 80.0 milliliters of a
0.150 molar solution of KI was electrolyzed for 3.00 minutes, using a constant current. At
the end of this time, the I
produced was titrated against a 0.225 molar solution of sodium
2
thiosulfate, which reacts with iodine according to the equation below. The end point of
the titration was reached when 37.3 milliliters of the Na
S
O
solution had been added.
2
2
3
→ 2 I
2-
-
2-
I
+ 2 S
O
+ S
O
2
2
3
4
6
(a) How many moles of I
was produced during the electrolysis?
2
(b) The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected over
water at 25˚C at a total pressure of 752 millimeters of mercury. Determine the
volume of hydrogen collected.
(The vapor pressure of water at 25˚C is 24 millimeters of
mercury.)
(c) Write the equation for the half–reaction that occurs at the anode during the
electrolysis.
(d) Calculate the current used during the electrolysis.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3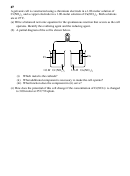 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8








