Redox And Electrochemistry Worksheet With Answer Key Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
#5
Explain each of the following.
(a) When an aqueous solution of NaCl is electrolyzed, Cl
is produced at the anode,
2 (g)
but no Na
is produced at the cathode.
(s)
(b) The mass of Fe
produced when 1 faraday is used to reduce a solution of FeSO
is
(s)
4
1.5 times the mass of Fe
produced when 1 faraday is used to reduce a solution of
(s)
FeCl
.
3
→ Zn
2+ (1–molar)
2+ (1–molar)
(c) Zn + Pb
+ Pb
2+
The cell that utilizes the reaction above has a higher potential when [Zn
] is decreased
2+
2+
and [Pb
] is held constant, but a lower potential when [Pb
] is decreased and
2+
[Zn
] is held constant.
(d) The cell that utilizes the reaction given in (c) has the same cell potential as another
2+
2+
cell in which [Zn
] and [Pb
] are each 0.1–molar.
#6
An unknown metal M forms a soluble compound, M(NO
)
.
3
2
(a) A solution of M(NO
)
is electrolyzed. When a constant current of 2.50 amperes is
3
2
applied for 35.0 minutes, 3.06 grams of the metal M is deposited. Calculate the
molar mass of M and identify the metal.
(b) The metal identified in (a) is used with zinc to construct a galvanic cell, as shown
below. Write the net ionic equation for the cell reaction and calculate the cell
potential, E˚.
+
-
K
Cl
Metal
Zinc
M
1.0 M M(NO )
1.0 M ZnSO
4
3 2
(c) Calculate the value of the standard free energy change, G˚, at 25˚C for the reaction
in (b).
(d) Calculate the potential, E, for the cell shown in (b) if the initial concentration of
ZnSO
is 0.10-molar, but the concentration of the M(NO
)
solution remains
4
3
2
unchanged.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3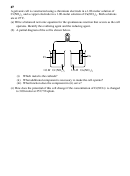 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8








