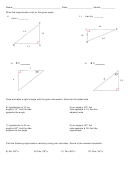
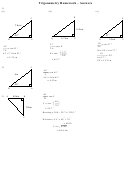
Trigonometry Worksheet Page 17
ADVERTISEMENT
Therefore,
sin { 2 { = 2 sin cos
$ $
#
= 2
%
%
& $
=
Also, we have
cos{2 { = cos
− sin
$
$
$
$
#
$ $
=
−
%
%
#
=
− = −
Why is cos{2 { negative? In this case, since
st
was in the 1
Quadrant, doubling its size evidently placed
the angle 2 into Quadrant 2, where the cosine is negative and the sine remains positive.
The Pythagorean Identity is
cos
+ sin
= 1.
$
$
Re-arranging or dividing through by terms produces many corollary forms of the Pythagorean Identity.
• The Pythagorean Identities and Corollaries
cos
+ sin
= 1
$
$
cos
= 1 − sin
(subtraction of sin
$
$
$
)
sin
= 1 − cos
(subtraction of cos
$
$
$
)
1 + tan
= sec
(divide through by cos
$
$
$
)
tan
= sec
− 1
$
$
(subtraction of 1)
cot
+ 1 = csc
(divide through by sin
$
$
$
)
cot
= csc
− 1
$
$
(subtraction of 1)
Example: The double angle identity for the cosine function is
cos{2 { = cos
− sin
$
$
.
Show that this formula can also be written as
1{ cos{2 { = 1 − 2 sin
$
2{ cos{2 { = 2 cos
− 1
$
Solution: In the first case (1), we substitute cos
with 1 − sin
$
$
and simplfy:
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14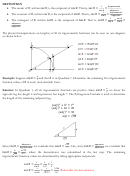 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22