Trigonometry Worksheet Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
For most other angles, a calculator is necessary to calculate the cosine, sine and tangent of an angle.
Example 6: A ray with an angle of 50° is drawn, with initial side being the positive x-axis. State the
point at which this ray intersects the circle, and the slope of this ray.
Solution: Using a calculator set to “Degree” mode, the x-coordinate is cos{50{ = 0.643 (rounded),
and the y-coordinate is sin { 50 { = 0.766 (rounded). The slope of the ray is tan { 50 { = 1.192
(rounded).
We can also observe some geometrical relationships between sine, cosine and tangent. First, we can view
the portion of the ray from the origin to the circle as a hypotenuse (of length 1) of a right triangle. The
legs have length cos (called the adjacent leg) and sin (called the opposite leg) (See Fig. 8).
Fig 8
Therefore, we can use the Pythagorean formula to form a relationship between cosine and sine:
{ adjacent leg {
+ { opposite leg {
= { hypotenuse {
$
$
$
{ cos {
+ { sin {
= 1
$
$
$
This is usually written as
cos
+ sin
= 1.
$
$
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6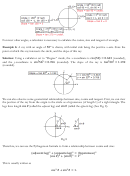 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14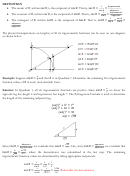 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22