Sample Comprehensive Review Of Academic Records Page 13
ADVERTISEMENT
Reference Sheet 4
Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency
Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills (BICS) is the everyday language that most children acquire through interacting
with family members and other children. ELLs acquire this in a few short years in English settings. It is often called
“playground language.”
Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP) is the language children need to be successful in the classroom. They
will not learn CALP on the playground and on average can take anywhere between 5-7 years to develop. CALP is not just
the highlighted vocabulary in a textbook that the publishing company suggests students pay special attention to. It
includes the academic words and sentence structures that we assume most native English speakers know, even though
they never use them outside the classroom. Other things to watch out for include idioms, acronyms, homophones,
homographs, and homonyms.
What is expected at each CALP level
Official
Beginning
Early Intermediate
Intermediate
Early Advanced
Advanced
Name
Definition Students demonstrate
Students demonstrate
Students demonstrate
Students demonstrate
Students comprehend
minimal comprehension of
increased comprehension
good comprehension of
consistent comprehension of
general and implied meaning,
general meaning.
of general meaning and
general meaningand
general meaning and good
including idiomatic and
Students follow basic
some specific meaning
increased comprehension
understanding of implied
figurative language.
instructions, respond
through participation using
of specific meaning by
meaning, orally and in writing,
Comprehension is
nonverbally or in single
key words and familiar
responding orally and in
in both context-embedded and
demonstrated in
words and phrases, and
phrases in face-to-face
written form (charts,
context-reduced situations.
decontextualized situations,
demonstrate different
interactions.
graphs, diagrams).
orally and in writing.
sounds.
Production
early: points to the bear
The bear is brown. He is
The brown bear lived with
Can bears live in the forest if
Would you like me to bring
Examples
later: brown, bear
eating.
his family in the forest.
they find food there?
pictures of the bear that I saw
last summer?
Oral
repeat; identify people,
recite familiar songs and
compare/contrast; identify
present, report; identify main
debate, evaluate, persuade,
Language
object, place; answer
poems; ask and answer
main points of a story;
idea and supporting details;
justify; explain common
Skills
yes/no, who, what, where
simple questions; role-play;
explain; describe; define
solicit information; analyze,
antonyms and synonyms;
retell; summarize
using content-related
hypothesize; identify antonyms
recognize multiple meanings
vocabulary
and synonyms; use affixes;
in text of familiar topic;
infer word meaning
understand, create jokes
Reading
use sound/symbol
read high frequency words,
read high frequency words,
read grade-level text with
read grade-level text with
Skills
relationships in known
contextualized vocabulary
contextualized vocabulary
English language development
English language
words and read high
and language structures in
and language structures in
(vocabulary & structure)
development (vocabulary and
frequency words
texts that are in familiar,
familiar text; read more
support through pre-teaching
structure) support through
patterned, and predictable
complex text from
pre-teaching
language experience
Writing
draw, circle, label, match;
write from own experience
write using frames or
compose with scaffolds
compose more complex
Skills
write simple sentences
using frames or simple
simple vignettes from
(formats, vocabulary webs)
writing using conventions
with frames
vignettes and word banks
experience with word
banks and other supports
Typical
0-6 months in U.S. school 6 mo.-1 yr. in U.S. school
1-3 years in U.S. school
3-5 years in U.S. school
5-7 years in U.S. school
Timeline
Please note individual progress depends on several factors, including previous schooling, acculturation, and motivation. Students with no prior school will take longer to progress through these stages
Adapted by Stacey Lee from ODE’s “Oregon English Language Proficiency Standards” 2004
Organized by Beth Hoecker-Martinez (LBLESD), Leah Hinkle (GAPS), Claudia Nunez (LBLESD), 2014
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9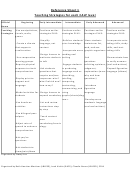 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18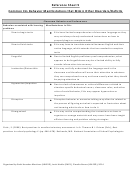 19
19 20
20








