Sample Comprehensive Review Of Academic Records Page 20
ADVERTISEMENT
Reference Sheet 10
Determining if a student has a Specific Learning Disability
REMEMBER: Gathering information prior to the referral is essential! Standardized testing can only show so much.
Spanish language cognitive assessments are not always appropriate
o Many students only receive instruction in English
Comparing scores on an English cognitive assessment to students who speak English at home is also not
appropriate
We use the Culture-Language Interpretive Matrix to determine if our cognitive assessments are valid measures of
their cognitive ability or if the scores are just measuring their language skills and knowledge of US culture.
Degree of cultural loading
Degree of linguistic demand
These subtests require more knowledge/experience with U.S. culture
These subtests require more language skills
Tests can be grouped according to their level of cultural loading and linguistic demand. Typically, scores of English
Language Learners gradually decrease in value as the linguistic demand and cultural loading increase (from the top-left
to the bottom-right of this chart).
Degree of Linguistic Demand
LOW
MEDIUM
HIGH
Fluid Reasoning A
74
Short-term Memory A
94
Short-term Memory C
74
Fluid Reasoning B
74
Processing Speed A
100
Visual Processing A
97
Processing Speed B
100
AVERAGE= 82
AVERAGE= 98
AVERAGE= 74
Long-term Memory A
85
Long-term Memory C
87
Long-term Memory B
97
Short-term Memory B
74
Visual Processing B
88
AVERAGE = 90
AVERAGE= 81
Comprehension/Knowledge A(Eng)
88
Comprehension/Knowledge B(Eng)
80
Comprehension/Knowledge C(Eng)
71
AVERAGE= 80
Our PSW (Patterns of Strengths and Weaknesses) evaluations look at the 7 broad areas of Cognitive Ability that make up
“IQ” to see if there is a research-based link between the area(s) of academic underachievement and the area(s) of
cognitive weakness. Your district may use a different method.
Cognitive Ability
Reading
Math
Writing
Fluid Reasoning: Problem solving with novel information. Recognize and understand
Moderate
STRONG
Moderate
relationships and patterns; inductive/deductive reasoning.
Comprehension/Knowledge: Breadth and depth of acquired knowledge. Primarily
STRONG
STRONG
STRONG
verbal, language-based knowledge.
Short-Term/Working Memory: Immediate recall of a sequence. Remember and
STRONG
STRONG
STRONG
reorganize information; requires divided attention.
Visual Processing: Ability to analyze/synthesize visual stimuli. Visual memory,
Moderate
Moderate
discrimination, and visual-spatial abilities.
Phonological/Auditory Processing: Ability to analyze/ synthesize auditory stimuli, and
STRONG
Moderate
discriminate sounds.
Long-Term Memory and Retrieval: Ability to store information in long-term memory,
STRONG
Moderate
and fluently retrieve new or acquired information.
Processing Speed: Mental quickness. Ability to fluently/automatically perform cognitive
STRONG
STRONG
STRONG
tasks, especially under pressure to maintain concentration.
Organized by Beth Hoecker-Martinez (LBLESD), Leah Hinkle (GAPS), Claudia Nunez (LBLESD), 2014
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9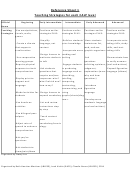 10
10 11
11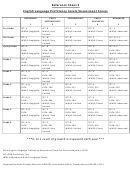 12
12 13
13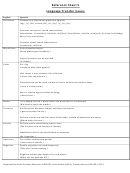 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20








