Circular Periodic Table Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
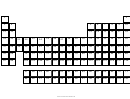
Circular Periodic Table
period – three elements atomic number 48 to 50.
d
2
period – four elements atomic number 75 to 78
f
1
period – four elements atomic number 107 to 110.
f
2
period – six elements atomic number 151 to 156.
g
1
period – six elements atomic number 201 to 206.
g
2
th
period – one element F atomic number 9.
7
head group in- p
1
period – one element Cl atomic number 17.
p
2
period – two elements atomic number 33 to 34.
d
1
period – two elements atomic number 51 to 52.
d
2
period – four elements atomic number 79 to 82.
f
1
period – four elements atomic number 111 to 114.
f
2
period – six elements atomic number 157 to 162.
g
1
period – six elements atomic number 207 to 212.
g
2
th
period – one element Ne atomic number 10.
8
head group in- p
1
period – one element Ar atomic number 18.
p
2
period – two elements atomic number 35 to 36.
d
1
period – two elements atomic number 53 to 54.
d
2
period – four elements atomic number 83 to 86.
f
1
period – four elements atomic number 115 to 118.
f
2
period – six elements atomic number 163 to 168.
g
1
period – six elements atomic number 213 to 218.
g
2
Miscellaneous group: It is also possible in future that some element will be discovered which have no
similarity with any elements, there is a miscellaneous group.
Border Line: The role of border line in the circular periodic table is separate to the group. If any group
fill up as your pre-decided limit as show in Fig-1 then the border line advise to go in upper period.
III.
CONCLUSION
The circular periodic table is most advantage for chemistry. It is international level solution because
about all type & properties adopted elements placed in it and we can already decide the position and nature of
new element.
REFERENCE
Mendleev’s periodic table is prescribed in 1869.
[1].
[2].
Long form of periodic table accepted by IUPAC in 1892.
Seaborg (ca. 2006). “transuranium element (chemical element)”. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
ab
[3].
^
^ “Extended elements: new periodic table”. 2010.
[4].
Pyykko, Pekka (2011). “A suggested periodic table up to Z< 172, based on Dirac-Fock calculations on atoms and ions”.
ab
[5].
^
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 13 (1): 161-8. Bibcode 2011PCCP…13…16IP. doi:10.1039/c0cp01575j. PMID 20967377.
[6].
^Eisberg, R.; Resnick, R. (1985). Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei and Partiles. Wiley.
37 | P a g e
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4