Inorganic Nomenclature
ADVERTISEMENT
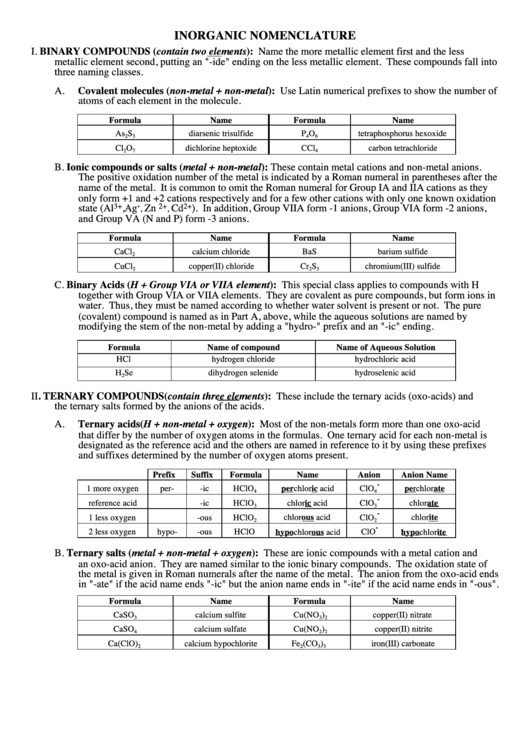
INORGANIC NOMENCLATURE
I.
BINARY COMPOUNDS (contain two elements): Name the more metallic element first and the less
metallic element second, putting an "-ide" ending on the less metallic element. These compounds fall into
three naming classes.
A.
Covalent molecules (non-metal + non-metal): Use Latin numerical prefixes to show the number of
atoms of each element in the molecule.
Formula
Name
Formula
Name
As
S
diarsenic trisulfide
P
O
tetraphosphorus hexoxide
2
3
4
6
Cl
O
dichlorine heptoxide
CCl
carbon tetrachloride
2
7
4
B.
Ionic compounds or salts (metal + non-metal): These contain metal cations and non-metal anions.
The positive oxidation number of the metal is indicated by a Roman numeral in parentheses after the
name of the metal. It is common to omit the Roman numeral for Group IA and IIA cations as they
only form +1 and +2 cations respectively and for a few other cations with only one known oxidation
3+
2+
2+
state (Al
, Ag
+
Zn
Cd
). In addition, Group VIIA form -1 anions, Group VIA form -2 anions,
,
,
and Group VA (N and P) form -3 anions.
Formula
Name
Formula
Name
CaCl
calcium chloride
BaS
barium sulfide
2
CuCl
copper(II) chloride
Cr
S
chromium(III) sulfide
2
2
3
C.
Binary Acids (H + Group VIA or VIIA element): This special class applies to compounds with H
together with Group VIA or VIIA elements. They are covalent as pure compounds, but form ions in
water. Thus, they must be named according to whether water solvent is present or not. The pure
(covalent) compound is named as in Part A, above, while the aqueous solutions are named by
modifying the stem of the non-metal by adding a "hydro-" prefix and an "-ic" ending.
Formula
Name of compound
Name of Aqueous Solution
HCl
hydrogen chloride
hydrochloric acid
H
Se
dihydrogen selenide
hydroselenic acid
2
II.
TERNARY COMPOUNDS (contain three elements): These include the ternary acids (oxo-acids) and
the ternary salts formed by the anions of the acids.
A.
Ternary acids (H + non-metal + oxygen): Most of the non-metals form more than one oxo-acid
that differ by the number of oxygen atoms in the formulas. One ternary acid for each non-metal is
designated as the reference acid and the others are named in reference to it by using these prefixes
and suffixes determined by the number of oxygen atoms present.
Prefix
Suffix
Formula
Name
Anion
Anion Name
-
1 more oxygen
per-
-ic
HClO
perchloric acid
ClO
perchlorate
4
4
-
reference acid
-ic
HClO
chloric acid
ClO
chlorate
3
3
-
1 less oxygen
-ous
HClO
chlorous acid
ClO
chlorite
2
2
-
2 less oxygen
hypo-
-ous
HClO
hypochlorous acid
ClO
hypochlorite
B.
Ternary salts (metal + non-metal + oxygen): These are ionic compounds with a metal cation and
an oxo-acid anion. They are named similar to the ionic binary compounds. The oxidation state of
the metal is given in Roman numerals after the name of the metal. The anion from the oxo-acid ends
in "-ate" if the acid name ends "-ic" but the anion name ends in "-ite" if the acid name ends in "-ous".
Formula
Name
Formula
Name
CaSO
calcium sulfite
Cu(NO
)
copper(II) nitrate
3
3
2
CaSO
calcium sulfate
Cu(NO
)
copper(II) nitrite
4
2
2
Ca(ClO)
calcium hypochlorite
Fe
(CO
)
iron(III) carbonate
2
2
3
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2