Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
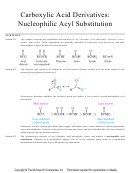
Lactams are cyclic amides.
Section 20.14
Like ester hydrolysis, amide hydrolysis can be achieved in either aqueous acid or aqueous base. The process is
Section 20.15
irreversible in both media. In base, the carboxylic acid is converted to the carboxylate anion; in acid, the
amine is protonated to an ammonium ion:
Nitriles are prepared by nucleophilic substitution (S N 2) of alkyl halides with cyanide ion, by converting
Section 20.16
aldehydes or ketones to cyanohydrins (Table 20.6), or by dehydration of amides.
The hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids is irreversible in both acidic and basic solution.
Section 20.17
Nitriles are useful starting materials for the preparation of ketones by reaction with Grignard reagents.
Section 20.18
Acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, and amides all show a strong band for CPO stretching in the infrared. The
Section 20.19
range extends from about 1820 cm 21 (acyl chlorides) to 1690 cm 21 (amides). Their 13 C NMR spectra are
characterized by a peak near d 180 for the carbonyl carbon. 1 H NMR spectroscopy is useful for distinguishing
between the groups R and R9 in esters (RCO 2 R9). The protons on the carbon bonded to O in R9 appear at
lower field (less shielded) than those on the carbon bonded to CPO.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1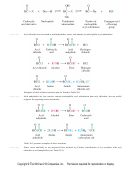 2
2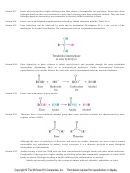 3
3 4
4








