Ph Chart - Chemistry Reference Sheet Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
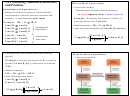
• The p-notation → pX = -log X
pOH = -log[OH
-
]
→ log[OH
] = -pOH ⇒ [OH
-
-
] = 10
-pOH
pK
= -log K
w
w
→ [H
← (take a -log)
O
+
][OH
-
] = K
3
w
→ -log[H
O
+
] + (-log[OH
-
]) = -log K
3
w
⇒ pH + pOH = pK
w
→ At 25°C, K
→ pK
= 1.0×10
-14
= 14.00
w
w
⇒ pH + pOH = 14.00
→ If pH = 7 → pOH = 7 → neutral solution
→
↑pOH);
Basic (↑pH, ↓pOH)
Acidic (↓pH,
K
and K
of a Conjugate Acid-Base Pair
Example:
A household ammonia solution has a
a
b
pH of 11.92. What is the pOH and the
• In a solution of the weak acid HA, both HA
concentration of OH
-
in it?
and its conjugate base, A
-
, react with water
→ pOH = 14.00 - pH = 14.00 – 11.92 = 2.08
↔
HA
+
H
O
A
-
+
H
O
+
K
(of HA)
2
3
a
→ [OH
-
] = 10
-pOH
= 10
-2.08
= 8.3×10
-3
↔
A
-
+
H
O
HA
+
OH
-
K
(of A
-
)
2
b
Note: The # of sig. figs in [OH
-
] (or [H
O
+
]) equals
3
↔
×K
+ →
H
O
+
H
O
H
O
+
+
OH
-
K
= K
the number of decimal places in pOH (or pH)
2
2
3
w
a
b
+
-
-
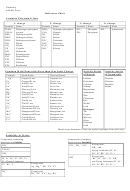
• Measuring pH in the laboratory
[H
O
][A
]
[HA][OH
]
×
=
×
=
+
=
-
K
K
3
[H
O
][OH
]
K
a
b
3
w
-
[HA]
[A
]
– Indicators – have different colors at different pH
×K
(pH paper, indicator solutions)
⇒For a conjugate acid-base pair →
K
= K
a
b
w
– pH meters – measure the pH by measuring the
K
K
-log
+ (-log
) = -log K
a
b
w
potential of a pH sensitive electrode immersed in
⇒ p
K
K
→ At 25°C, p
K
K
+ p
= pK
+ p
= 14.00
the solution (more accurate)
a
b
a
b
w
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3