Ph Chart - Chemistry Reference Sheet Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
The stronger the
18.3 Relative Acid-Base Strength and the
acid, the weaker its
Net Direction of Reaction
conjugate base and
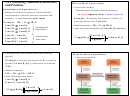
• An acid-base reaction proceeds to a greater
vice versa
extent from the stronger acid and stronger base
↑K
⇔ ↓K
towards the weaker acid and weaker base
a
b
↔
HA
+
B
A
-
+
HB
+
↓pK
⇔ ↑pK
a
b
→
stronger acid
+
stronger base
weaker base
+
weaker acid
Example:
The K
of
→The reaction is shifted towards A
-
and HB
+
(K
> 1)
a
c
HF is 6.8×10
-4
. What
Examples:
is the K
of F
-
?
b
↔
HF
+
NH
F
-
+
NH
+
3
4
K
= K
/ K
=
→
stronger acid
+
stronger base
weaker base
+
weaker acid
b
w
a
= 1.0×10
-14
/6.8×10
-4
↔
-
+
HF
+
H
O
F
+
H
O
2
3
K
= 1.5×10
-11
←
b
weaker acid
+
weaker base
stronger base
+
stronger acid
Example:
-4
-10
Given K
= 6.8×10
and K
= 6.2×10
,
(HF)
(HCN)
a
a
determine the preferred direction of the reaction
+ HCN ↔ HF + CN
F
-
-
→ Compare the strengths of the acids on both sides
→ HF is stronger than HCN (HF has higher K
value)
a
→ Compare the strengths of the bases on both sides
→ Since HF is a stronger acid than HCN, the
conjugate base of HF, F
-
, is a weaker base than the
conjugate base of HCN, CN
-
→ CN
-
is stronger than F
-
(CN
-
has higher K
value)
b
⇒
↔
F
-
+
HCN
HF
+
CN
-
is shifted to the left (K
<1)
c
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3