Modeling Meiosis
ADVERTISEMENT
Modeling Meiosis with Pop Beads
In this exercise, you will study the process of meiosis using chromosome simulation kits. The diploid cell you
will be modeling is greatly simplified, with only one pair of homologous chromosomes (2n = 2).
Procedure
Constructing Chromosomes
Assemble two strands of yellow beads connected to magnetic centromeres and two strands of red beads
connected to magnetic centromeres. One of the red strands represents the chromosome contribution of the
female parent, and one of the yellow strands represents the chromosome contribution of the male parent.
These two strands represent homologous chromosomes. The second red and yellow strands are to be used as
sister chromatids for each of these chromosomes.
Interphase - Significant Event: DNA Replication
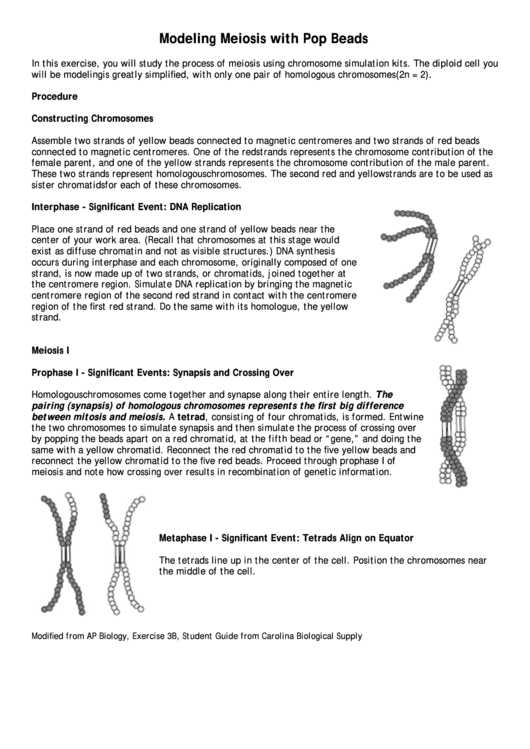
Place one strand of red beads and one strand of yellow beads near the
center of your work area. (Recall that chromosomes at this stage would
exist as diffuse chromatin and not as visible structures.) DNA synthesis
occurs during interphase and each chromosome, originally composed of one
strand, is now made up of two strands, or chromatids, joined together at
the centromere region. Simulate DNA replication by bringing the magnetic
centromere region of the second red strand in contact with the centromere
region of the first red strand. Do the same with its homologue, the yellow
strand.
Meiosis I
Prophase I - Significant Events: Synapsis and Crossing Over
Homologous chromosomes come together and synapse along their entire length. The
pairing (synapsis) of homologous chromosomes represents the first big difference
between mitosis and meiosis. A tetrad, consisting of four chromatids, is formed. Entwine
the two chromosomes to simulate synapsis and then simulate the process of crossing over
by popping the beads apart on a red chromatid, at the fifth bead or “gene,” and doing the
same with a yellow chromatid. Reconnect the red chromatid to the five yellow beads and
reconnect the yellow chromatid to the five red beads. Proceed through prophase I of
meiosis and note how crossing over results in recombination of genetic information.
Metaphase I - Significant Event: Tetrads Align on Equator
The tetrads line up in the center of the cell. Position the chromosomes near
the middle of the cell.
Modified from AP Biology, Exercise 3B, Student Guide from Carolina Biological Supply
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2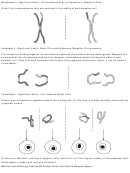 3
3 4
4








