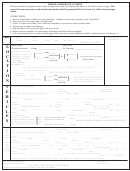
Person Centered Employment Plan Form Page 24
ADVERTISEMENT
Section 8 - Social Security Work Incentives
Terms:
o Substantial Gainful Activity (SGA) for a non-blind individual = $1070.
o Substantial Gainful Activity (SGA) for a blind individual = $1800.
o Trial Work Period Amount (TWP Amount) = $770.
o Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI).
o Supplemental Security Income (SSI).
Income and SSI:
If you receive SSI and plan to work, the income you earn will reduce the amount of your monthly SSI
benefit. There are special programs known as “work incentives.” These programs allow a person
receiving SSI to work and continue to receive all or part of their disability payments as well as maintain
eligibility for Medicare and/or Medicaid.
Work Incentives for SSDI Only:
TRIAL WORK PERIOD (TWP)
The Trial Work Period allows you to test your ability to work by providing a period of 9 months of gross
earnings during which your SSDI check is not affected. A month does not count towards your trial
work period unless your gross earnings meet or exceed an amount set each year by SSA. In 2014, the
TWP amount is $770. During your trial work period, you will receive your full disability benefit
regardless of how much you earn. You must report your work activity to SSA and continue to have a
disabling impairment. The 9 months does not need to be consecutive, they are counted within a five-
year period. Certain other rules apply. Medicare coverage will continue for 93 months after the last
month of the TWP.
EXTENDED PERIOD OF ELIGIBILITY (EPE)
The Extended Period of Eligibility begins after you have completed your trial work period and have
gross earnings at or above the SGA level. The EPE lasts for 36 months and allows you to receive your
SSDI check in any month that your earnings fall below SGA. If work is discontinued during the EPE, you
only need to contact SSA and ask for a reinstatement of benefits. You must continue to have a
disabling impairment.
SUBSIDY OR SPECIAL CONDITIONS
A subsidy is defined as the value of extra support a person receives on the job. The subsidy is provided
by the employer and the worker must earn the same pay as other workers doing the same job.
Examples include a job coach, mentor, extra supervision, or a reduced workload. The employer
determines the value of the subsidy. Special conditions apply when the individual is not fully earning
his or her wages because the work is performed under special conditions such as on the job coaching
or substitution in which the job coach performs part or all of the individual’s job duties. SSA will
deduct the wages that are not considered “earned” by the individual.
Examples of subsidies:
• You receive more supervision than other workers who are doing the same or a similar job for
the same pay.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29