Problems For Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Chemistry Worksheet With Answers Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
5. The numbers represent approximate pK
values for the substances acting as acids.
a
CN
+
NH
HCN
+
NH
3
2
9
38
O
O
+
+
OH
O
H
C
CH
H
C
CH
3
2
3
3
17
20
H
O +
H
O
+
NH
NH
2
3
2
3
-
4
1.7
H
CO
+ H
O
HCO
+
H
O
2
3
2
3
3
-
6.4
1.7
CH
CH
CH
CH
+
CH
CH
CH
CH
CH
+
CH
3
2
2
3
3
2
2
2
2
3
40
48
6. A
7. Methanesulfonic acid is the stronger acid. The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid. A
lower pKa is associated with a larger Ka which signifies greater dissociation. The large
relative difference in acidity in this case can be most easily seen by gauging the relative
basicities of the conjugate bases. The weaker the base, the stronger the corresponding
- , is considerably stabilized by resonance
conjugate acid. Methanesulfonate, CH
SO
3
3
O - . This effect greatly reduces the
delocalization which is not found in ethoxide, CH
CH
3
2
basicity of methanesulfonate relative to ethoxide. Draw the Lewis formula for
methanesulfonate and the resonance forms for practice.
8. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is a stronger acid. Compare the strengths of the
conjugate bases and remember that the weaker the base, the stronger the conjugate
acid. Both bases are stabilized by resonance, but in the case of the trifluoro derivative,
the presence of the highly electronegative fluorine atoms serves to delocalize the
negative charge to an even greater extent by the inductive effect of fluorine. This
additional delocalization makes trifluoromethanesulfonate a weaker base.
COO - < CH
O - < NH
-
9. CH
3
3
2
first factor to consider is the nature of the atom which bears the negative charge. The
more electronegative the atom that bears the negative charge, the more stable the
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4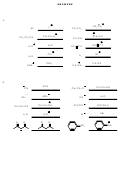 5
5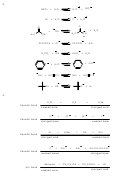 6
6 7
7 8
8