Genetics Problem Sets Worksheet With Answer Key Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
b. Carry out to the F 2 generation the reciprocal cross to the above. (Start with a normal
homozygous female and a bobbed male in the P 1 .) Show all genotypes, phenotypes,
and expected fractions or percents. At what point in the cross do the results show
you that this cross is sex-linked instead of a normal (autosomal) cross?
4. BAR EYES
A rare mutation in fruit flies produces eyes with an unusual shape called "bar eyes." Explain
the mechanism of this gene based on the following results of a fruit fly cross. The crosses and
resulting number of offspring are shown below. Your task is to figure out the genotypes of all
involved. Hint: To answer this, you'll need to:
1. Set up a key, guessing which trait is dominant
2. Carry out the crosses
3. Compare your expected results (that you figured out on paper) with the "actual" results
(calculated from the numbers shown below)
4. If your results don't match the ones given below, then you did something wrong. Go back
and change something in your "test cross"
P 1
NORMAL FEMALE
X
BAR-EYED MALE (both true-breeding)
F 1
32 BAR-EYED FEMALES and 35 NORMAL MALES
F 2
28 BAR-EYED FEMALES
31 NORMAL FEMALES
29 BAR-EYED MALES
30 NORMAL MALES
Genetics Problems
9
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8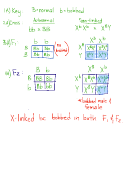 9
9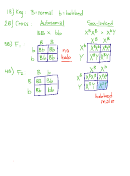 10
10 11
11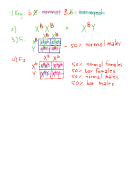 12
12 13
13 14
14