Genetics Problem Sets Worksheet With Answer Key Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Genetics Problems Set #1
MONOHYBRID CROSS (Simple dominance)
Because we are examining the inheritance of only a single trait (i.e. height), we call this
type of cross a monohybrid cross. When we work a cross we are determining the
possible combinations of alleles that could be present in the offspring (children) of the
parents. Since meiosis creates gametes with the haploid number of chromosomes- only
one allele for each trait can be present in a gamete-- for example "D" or "d".
1. In peas, green pod color is dominant to yellow pod color. Show a cross between true-
breeding green and true-breeding yellow plants (P 1 generation). Carry out the cross
through the F 1 and F 2 generations. Show the fractions or percents of phenotypes and
genotypes for all generations.
2. Consider blue eyes in humans to be recessive to brown eyes. Show the expected
children of a blue-eyed woman with a brown-eyed man whose mother had blue eyes.
Include the fractions or percents of all genotypes and phenotypes. State what you
know (and don't know) about the brown-eyed man's father based on the information
given here. What can you predict about the brown-eyed man's brothers and sisters?
3. In poultry, rose comb is dominant to single comb.
a. Cross a true-breeding rose-combed rooster with a single-combed hen. Then
cross the F 1 's to produce an F 2 generation. Show the fractions or percents of all
genotypes and phenotypes.
b. Explain how it is possible for a rose-combed rooster and a rose-combed hen to
produce single-combed offspring. What percentage of the offspring is expected
to have single combs in this cross?
4. In humans the ability to roll one's tongue is dominant to the inability to do so.
a. Show the expected offspring of a cross between a heterozygous roller and a
homozygous roller. Include genotypes, phenotypes, and their associated
fractions or percents.
4b. Explain how it is possible for a "roller" man and a "non-roller" woman to produce
a roller son, then a non-roller son, then a non-roller daughter. What is the
probability that their next child will be a roller? What is the probability that their
next child will be a roller daughter? (Consider both the phenotype and the sex of
the child in determining the probability.)
Genetics Problems
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8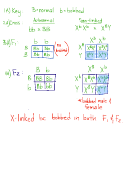 9
9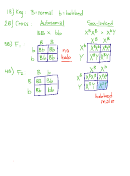 10
10 11
11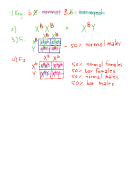 12
12 13
13 14
14