Genetics Problem Sets Worksheet With Answer Key Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
1. HEMOPHILIA
Most people’s blood clots normally. Hemophilia is a blood disorder that causes blood not
to clot properly. The allele for hemophilia is recessive to the allele for normal blood
clotting. These alleles are located on the human X chromosome. The Y chromosome is a
genetic "blank" for this trait; it contains no allele for the blood-clotting gene.
A number of cases of hemophilia have occurred among male descendants in the
family of England's Queen Victoria. She, however, did not have hemophilia.
(Queen Victoria lived during the time of Charles Darwin.)
a. Show the genotypes of parents that would produce a male descendant with
hemophilia (when the mother does not have hemophilia).
b. Show the genotype required of parents to produce a hemophiliac daughter.
c. Explain what's wrong with the statement "That hemophiliac man's father was also a
hemophiliac, so he must have inherited the disease from his father."
2. RED-GREEN COLOR BLINDNESS
Red/green color-blindness in humans is recessive and X-linked (same inheritance pattern
as hemophilia).
a. A woman has normal vision, but her father is color-blind. Is she necessarily a carrier
(heterozygous)? Explain.
b. Diagram all genotypes and phenotypes of parents and expected children in a family
where the woman has normal vision and no family history of color blindness, and the
man is color-blind.
c. In a large family, all nine sons were color-blind and all four daughters had normal
vision. Give the genotypes and phenotypes of all concerned.
3. BOBBED HAIRS
The trait called "bobbed hairs" in the fruit fly (Drosophila) is recessive and is located on the
X chromosome only. Assume all flies are true-breeding.
a. Carry out to the F 2 generation a cross between a bobbed female and a wild type
(normal) male. Show all genotypes, phenotypes, and expected fractions or percents.
At what point in the cross (at which generation) do the results show you that this
cross is sex-linked instead of a normal (autosomal) cross. (Hint: To answer this, you'll
need to carry out this problem, to the F
generation, as if it is normal (autosomal) AND as if it
2
were sex-linked. Then you should compare your F
and F
results. So the question is asking,
1
2
at which generation, F
or F
, do the results come out differently if autosomal or if sex-
1
2
linked?)
Genetics Problems
8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8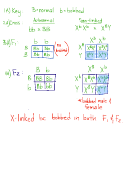 9
9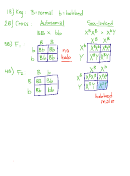 10
10 11
11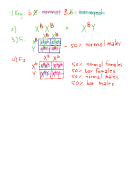 12
12 13
13 14
14