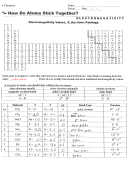
Chemistry Unit C1 Worksheet - Study And Revision Pack (Foundation Paper) Page 25
ADVERTISEMENT
5.15 Demonstrate an understanding that the proportion of carbon
dioxide in the atmosphere varies, due to human activity, and
that chemists are investigating methods to control the amount of
the gas in the atmosphere by:
a iron seeding of oceans
b converting carbon dioxide into hydrocarbons
5.16 Evaluate how far the correlation between global temperature
and the proportion of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere provides
evidence for climate change
5.17 Describe biofuels as being possible alternatives to fossil fuels
5.18 Recall that one example of a biofuel is ethanol obtained by
processing sugar cane or sugar beet and that it can be used to
reduce the demand for petrol
5.19 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of replacing fossil
fuels with biofuels, including:
a the fact that biofuels are renewable
b that growing the crops to make biofuels requires land and
may affect the availability of land for growing food
c the balance between the carbon dioxide removed from the
atmosphere as these crops grow and the carbon dioxide
produced when they are transported and burned
5.20 Demonstrate an understanding of the factors that make a good
fuel, including:
a how easily it burns
b the amount of ash or smoke it produces
c the comparative amount of heat energy it produces
(calculations involving conversion to joules are not required)
d how easy it is to store and transport
5.21 Recall that a simple fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to
form water and that this reaction releases energy
5.22 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using hydrogen,
rather than petrol, as a fuel in cars
5.23 Describe petrol, kerosene and diesel oil as non-renewable fossil
fuels obtained from crude oil and methane as a non-renewable
fossil fuel found in natural gas
5.24 Compare the temperature rise produced when the same volume
of water is heated by different fuels
5.25 Recall that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, which are
present in crude oil
5.26 Recall the formulae of the alkanes methane, ethane and
propane, and draw the structures of these molecules to show
how the atoms are bonded together (no further knowledge of
bonding is required in this unit)
5.27 Recall that alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons
5.28 Recall the formulae of the alkenes ethene and propene and draw
the structures of their molecules to show how the atoms are
bonded together
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26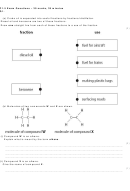 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34