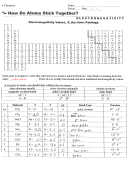
Chemistry Unit C1 Worksheet - Study And Revision Pack (Foundation Paper) Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
Revised
C1 Specification
1
2
3
2.1 Describe that igneous rocks, such as granite, are:
a formed by the solidification of magma or lava
b made of crystals whose size depends on the rate of cooling
2.2 Describe chalk and limestone as examples of sedimentary rocks
2.3 Describe how sedimentary rocks are formed by the compaction
of layers of sediment over a very long time period
2.4 Recall that sedimentary rocks:
a may contain fossils
b are susceptible to erosion
2.5 Describe marble as an example of a metamorphic rock
2.6 Describe the formation of metamorphic rocks by the action of
heat and/or pressure, including the formation of marble from
chalk or limestone
2.7 Recall that limestone, chalk and marble exist in the Earth’s crust
and that they are all natural forms of calcium carbonate
2.8 Demonstrate an understanding of the balance between the
demand for limestone and the economic, environmental and
social effects of quarrying it
2.9 Demonstrate an understanding of the commercial need for
quarrying calcium carbonate on a large scale, as a raw material,
for the formation of glass, cement and concrete
2.10 Describe the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate into
calcium oxide and carbon dioxide
2.11 Investigate the ease of thermal decomposition of carbonates,
including calcium carbonate, zinc carbonate and copper carbonate
2.12 Describe the ease of thermal decomposition of different metal
carbonates
2.13 Demonstrate an understanding that:
a atoms are the smallest particles of an element that can take
part in chemical reactions
b during chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor
destroyed
c during chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged to make
new products with different properties from the reactants
2.14 Describe the effect of water on calcium oxide
2.15 Describe how calcium hydroxide dissolves in water to form a
solution, known as limewater
2.16 Demonstrate an understanding that the total mass before and
after a reaction in a sealed container is unchanged, as shown
practically by a precipitation reaction
2.17 Explain how calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide and calcium
carbonate can be used to neutralise soil acidity
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26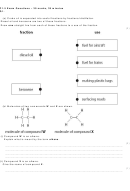 27
27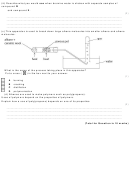 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34