3.1 Quadratic Functions Examples And Worksheet - Chapter 3: Polynomial And Rational Functions Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
333371_0301.qxp
12/27/06
1:20 PM
Page 255
255
Section 3.1
Quadratic Functions
The Standard Form of a Quadratic Function
E x p l o r a t i o n
The equation in Example 1(d) is written in the standard form
Use a graphing utility to graph
2
y
ax
with
a
2,
1,
2
f x
a x
h
k.
0.5,
0.5, 1,
and 2. How does
This form is especially convenient for sketching a parabola because it identifies
changing the value of affect
a
the vertex of the parabola as h, k .
the graph?
Use a graphing utility to
2
graph
y
x
h
with
Standard Form of a Quadratic Function
h
4,
2,
2, and 4. How
The quadratic function given by
does changing the value of
h
affect the graph?
2
f x
a x
h
k,
a
0
Use a graphing utility
is in standard form. The graph of is a parabola whose axis is the vertical
f
2
to graph
y
x
k
with
line
x
h
and whose vertex is the point
h, k .
If
a > 0,
the parabola opens
k
4,
2, 2,
and 4. How
upward, and if
a < 0,
the parabola opens downward.
does changing the value of
k
affect the graph?
Example 2
Identifying the Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Prerequisite Skills
2
Describe the graph of
f x
2x
8x
7
and identify the vertex.
If you have difficulty with this example,
Solution
review the process of completing the
square for an algebraic expression in
Write the quadratic function in standard form by completing the square. Recall
Section 2.4, paying special attention
2
that the first step is to factor out any coefficient of
x
that is not 1.
to problems in which a
1.
2
f x
2x
8x
7
Write original function.
2
2x
8x
7
Group -terms.
x
2
2 x
4x
7
Factor 2 out of -terms.
x
2
Add and subtract
4 2
4
within
2
2 x
4x
4
4
7
parentheses to complete the square.
2
4
f(x) = 2x
+ 8x + 7
2
2
4
2
2 x
4x
4
2 4
7
Regroup terms.
2
2 x
2
1
Write in standard form.
−6
3
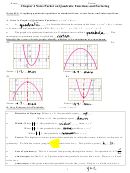
From the standard form, you can see that the graph of is a parabola that opens
f
(−2, −1)
upward with vertex
2,
1 ,
as shown in Figure 3.5. This corresponds to a left
−2
shift of two units and a downward shift of one unit relative to the graph of
2
y
2x
.
Figure 3.5
Now try Exercise 13.
2
To find the -intercepts of the graph of
x
f x
ax
bx
c,
solve the equa-
2
tion
ax
2
If
ax
bx
c
does not factor, you can use the
bx
c
0.
Quadratic Formula to find the -intercepts, or a graphing utility to approximate
x
the -intercepts. Remember, however, that a parabola may not have -intercepts.
x
x
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11