Mod 5 Revision Guide 1. Thermodynamics Worksheet With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
1: THERMODYNAMICS
Definitions of enthalpy changes
Enthalpy change of formation
The standard enthalpy change of formation of a compound is the energy transferred when 1
mole of the compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions (298K and
100kpa), all reactants and products being in their standard states
-1
Na (s) + ½Cl
(g)
NaCl (s)
[∆H
= - 411.2 kJ mol
]
2
f
Enthalpy of atomisation
The enthalpy change for a solid metal turning to
gaseous atoms can also be called the Enthalpy of
The enthalpy of atomisation of an element is the enthalpy change
sublimation and will numerically be the same as
when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the element
the enthalpy of atomisation
in its standard state
-1
Na (s)
Na(g) [∆Hsub = +148 kJ mol
]
-1
Na (s)
Na(g) [∆H
= +148 kJ mol
]
at
-1
½ O
(g)
O (g) [∆H
= +249 kJ mol
]
2
at
For diatomic molecules the ∆Hdiss of the
Bond dissociation enthalpy (bond energy)
molcule is the same as 2x ∆H
of the element
The bond dissociation enthalpy is the standard molar enthalpy
at
change when one mole of a covalent bond is broken into
∆H
-1
Cl
2Cl
= +242 kJ mol
2 (g)
(g)
diss
two gaseous atoms (or free radicals)
∆H
-1
½ Cl
Cl
= +121 kJ mol
∆H
-1
Cl
2Cl
= +242 kJ mol
2 (g)
(g)
at
2 (g)
(g)
diss
Or
∆H
-1
CH
CH
+ H
= +435 kJ mol
4 (g)
3 (g)
(g)
diss
First Ionisation enthalpy
Second Ionisation enthalpy
The second ionisation enthalpy is the enthalpy change to
The first ionisation enthalpy is the enthalpy change
remove 1 mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous 1+
required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of
ions to produces one mole of gaseous 2+ ions.
gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a +1
+
2+
-
Mg
(g)
Mg
(g) + e
[∆ Hi]
charge
+
-
Mg (g)
Mg
(g) + e
[∆H IE]
First Electron affinity
second electron affinity
The first electron affinity is the enthalpy change that occurs
The second electron affinity is the enthalpy change when
when 1 mole of gaseous atoms gain 1 mole of electrons to
one mole of gaseous 1- ions gains one electron per ion to
form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a –1 charge
produce gaseous 2- ions.
-
-
-1
O (g) + e
O
(g)
[∆Hea] = -141.1 kJ mol
]
–
-
2-
-1
O
(g) + e
O
(g)
[∆Hea = +798 kJ mol
]
The first electron affinity is exothermic for atoms that
The second electron affinity for oxygen is endothermic
normally form negative ions because the ion is more stable
because it take energy to overcome the repulsive force
than the atom and there is an attraction between the
between the negative ion and the electron
nucleus and the electron
Enthalpy of lattice formation
Enthalpy of lattice dissociation
The Enthalpy of lattice formation is the standard enthalpy
The Enthalpy of lattice dissociation is the standard enthalpy
change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal lattice is formed
change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal lattice form is
from its constituent ions in gaseous form.
separated into its constituent ions in gaseous form.
+
-
-1
+
-
-1
Na
(g) + Cl
(g)
NaCl (s)
[∆H
= -787 kJ mol
]
NaCl (s)
Na
(g) + Cl
(g) [∆H
= +787 kJ mol
]
Latt
Latt
Note the conflicting definitions and the sign that always accompanies the definitions
Enthalpy of Hydration ∆ ∆ ∆ ∆ H
Enthalpy of solution
hyd
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions
The enthalpy of solution is the standard enthalpy change
become aqueous ions .
when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in an large
∆H
+
+
+
-1
X
+ aq
X
For Li
= -519 kJ mol
enough amount of water to ensure that the dissolved ions
(g)
(aq)
hyd
or
are well separated and do not interact with one another
∆H
-
-
-1
X
+ aq
X-
For F
= -506 kJ mol
(g)
(aq)
hyd
+
-
NaCl (s) + aq
Na
(aq) + Cl
(aq)
This always gives out energy (exothermic, -ve) because
bonds are made between the ions and the water molecules
N Goalby
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3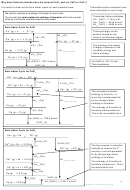 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9