Mod 5 Revision Guide 1. Thermodynamics Worksheet With Answers Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
Free-energy change (∆ ∆ ∆ ∆ G) and entropy change (∆ ∆ ∆ ∆ S)
A SPONTANEOUS PROCESS (e.g. diffusion) will proceed on its
own without any external influence.
Activation
Energy:
A problem with ∆H
E
A
reactants
A reaction that is exothermic will result in products that
are more thermodynamically stable than the reactants.
This is a driving force behind many reactions and causes
∆H
them to be spontaneous (occur without any external
products
influence).
Progress of Reaction
Some spontaneous reactions, however, are endothermic.
How can this be explained?
We need to consider something called entropy
Entropy is a description of the number of
Entropy, S˚
ways atoms can share quanta of energy.
If number of ways of arranging the energy
Substances with more ways of arranging their atoms and
(W) is high, then system is disordered
energy (more disordered) have a higher entropy.
and entropy (S) is high.
Elements
Compounds
gas
…tend to have lower
Simpler compounds
Complex compounds
entropies than…
Pure substances
Mixtures
boiling
Liquid
melting
Solids have lower entropies than liquids which are lower than gases.
solid
When a solid increases in Temperature its entropy increases as the
particles vibrate more.
Temperature
There is a bigger jump in entropy with boiling than that with melting.
Gases have large entropies as they are much more disordered
At 0K substances have zero
entropy. There is no disorder
as particles are stationary
Predicting Change in entropy ‘∆S’ Qualitatively
An increase in disorder and entropy will lead to a positive entropy change ∆S˚ = +ve
In general, a significant increase in the entropy will occur if:
Balanced chemical equations can
-there is a change of state from solid or liquid to gas
often be used to predict if ∆S˚ is
- there is a significant increase in number of molecules
positive or negative.
between products and reactants.
NH
Cl (s)
HCl (g) + NH
(g)
Na
+ ½ Cl
NaCl
4
3
s
s
2 g
∆S˚ = +ve
∆S˚ = -ve
•change from solid reactant to gaseous products
•change from gaseous and solid reactant to solid
•increase in number of molecules
•decrease in number of molecules
both will increase disorder
both will decrease disorder
Calculating ∆S˚ quantitatively
Elements in their standard
Data books lists standard entropies (S˚) per mole for a variety of substances.
states do not have zero
It is not possible for a substance to have a standard entropy of less than zero.
entropy. Only perfect
crystals at absolute zero
(T = 0 K) will have zero
-1
-1
The unit of entropy is J K
mol
∆S˚ = Σ S˚
- ΣS˚
entropy:
products
reactants
5
N Goalby
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3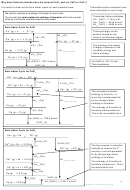 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9