Mod 5 Revision Guide 1. Thermodynamics Worksheet With Answers Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
Example .
Hydration enthalpies are exothermic as energy is given
Calculate the enthalpy of solution of NaCl
given that the lattice enthalpy of formation of
out as water molecules bond to the metal ions.
-1
NaCl is -771 kJmol
and the enthalpies of
+
The negative ions are attracted to the δ
hydrogens on
hydration of sodium and chloride ions are -406
the polar water molecules and the positive ions are
-1
and -364 kJmol
respectively
-
attracted to the δ
oxygen on the polar water molecules.
∆
∆ H
Σ∆H
= -
+
H sol
formation
hyd
Latt
= - (-771) + (-406-364)
-1
= + 1 kJmol
ΔH
endothermic.
solution
2+
2-
Ba
(g)
+ SO
(g)
4
∆H
2+
Ba
The higher the charge density the greater the hydration
hyd
∆H
+ ∆H
2-
SO
enthalpy (e.g. smaller ions or ions with larger charges)
lattice dissociation
4
hyd
(BaSO
)
4
as the ions attract the water molecules more strongly.
2+
2-
Ba
(aq)
+ SO
(aq)
4
e.g. Fluoride ions have more negative hydration
ΔH
solution
BaSO
(s)
INSOLUBLE
enthalpies than chloride ions
4
Magnesium ions have a more negative hydration enthalpy
than barium ions
What does ΔH
tell us?
Solution
Generally ΔH
is not very exo or endothermic so the hydration enthalpy is about the same as lattice
solution
enthalpy.
In general the substance is more likely to be soluble if the ΔH
is exothermic.
solution
If a substance is insoluble it is often because the lattice enthalpy is much larger than the hydration enthalpy and
it is not energetically favourable to break up the lattice, making ΔH
endothermic.
solution
We must consider entropy, however, to give us the full picture about solubility.
When a solid dissolves into ions the entropy increases as there is more disorder as solid changes to solution
and number of particles increases.
This positive ∆S can make ∆G negative even if ∆H solution is endothermic, especially at higher temperatures.
For salts where ΔH solution is exothermic
For salts where ΔH solution is endothermic
the salt will always dissolve at all Temperatures
the salt may dissolve depending on whether the
-T∆S value is more negative than ∆H is positive
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
∆G is
∆S is positive due to the
∆H is
Will dissolve
always
increased disorder as more
∆S is positive due to
if ∆G is
negative
negative
particles so - T∆S always
∆H is
the increased
negative
negative
positive
disorder as more
particles so - T∆S
always negative
Increasing the Temperature will make it more
likely that ∆G will become negative, making the
reaction feasible and the salt dissolve
N Goalby
8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3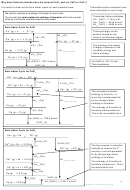 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9