Mod 5 Revision Guide 1. Thermodynamics Worksheet With Answers Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Born Haber cycle: calcium oxide
Notice the second electron affinity for
2+
2-
Ca
(g) + O
(g)
oxygen is endothermic because it
+
2+
-
Ca
(g) + 2e
O (g)
take energy to overcome the
∆H
(O)
∆H
repulsive force between the
Ea2
(O)
Ea1
∆H
negative ion and the electron
(O)
at
2+
-
-
Ca
(g)
+ e
+ O
(g)
2+
-
Ca
(g) + 2e
+ ½ O
(g)
2
∆H
(Ca)
IE 2
In this case the cycle has been
+
-
Ca
(g) + e
+ ½ O
(g))
constructed using
2
∆H
lattice dissociation
∆H
(Ca)
The calculation therefore is:
IE 1
(∆H
(CaO) + ∆H
=
Ca (g)
+ ½ O
(g)
f
lattice dissociation )
∆H
2
Ca + ∆H
Ca + ∆H
lattice dissociation
(∆H
Ca +
atm
IE 1
IE 2
∆H
O+ ∆H
O + ∆H
O )
∆H
atm
Ea1
Ea2
(Ca)
at
Ca (s) + ½ O
(g)
2
∆H
(CaO)
f
CaO (s)
Trends in Lattice Enthalpies
The lattice enthalpies become
The strength of a enthalpy of lattice formation depends on the following
less negative down any group.
factors
e.g. LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl
1.
The sizes of the ions:
e.g group 1 halides (eg NaF KI) have
The larger the ions, the less negative the enthalpies of lattice
lattice enthalpies of around –700 to -
formation (i.e. a weaker lattice). As the ions are larger the charges
1000
become further apart and so have a weaker attractive force
group 2 halides (eg MgCl
) have lattice
2
between them.
enthalpies of around –2000 to –3500
2.
The charges on the ion:
group 2 oxides eg MgO have lattice
enthalpies of around –3000 to –4500
The bigger the charge of the ion, the greater the attraction between
-1
kJmol
the ions so the stronger the lattice enthalpy (more negative values).
There is a tendency towards covalent
Perfect Ionic Model
character in ionic substances when
•the positive ion is small
Theoretical lattice enthalpies assumes a perfect ionic model where
•the positive ion has multiple charges
the ions are 100% ionic and spherical and the attractions are
•the negative ion is large
purely electrostatic.
•the negative ion has multiple negative
charges.
Differences between theoretical and Born Haber (experimental)
lattice enthalpies
When a compound has some covalent
character- it tends towards giant
The Born Haber lattice enthalpy is the real experimental value.
covalent so the lattice is stronger than
When a compound shows covalent character, the theoretical and the
if it was 100% ionic. Therefore the born
born Haber lattice enthalpies differ. The more the covalent character
haber value would be larger than the
the bigger the difference between the values.
theoretical value.
When the negative ion becomes distorted and more covalent we say it becomes polarised. The
metal cation that causes the polarisation is called more polarising if it polarises the negative ion.
Ionic with covalent
-
+
100% ionic
character
When 100 % ionic the ions are spherical.
The charge cloud is distorted .The theoretical
The theoretical and the born Haber lattice
and the experimental Born Haber lattice
3
enthalpies will be the same
enthalpies will differ
N Goalby
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3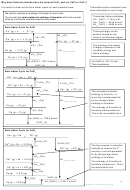 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9