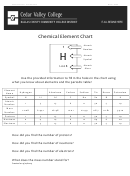
Chapter 2 An Introduction To Chemistry - The Structure Of Matter And The Chemical Elements Worksheet Page 26
ADVERTISEMENT
58
Chapter 2
The Structure of Matter and the Chemical Elements
Chapter
Model A simplified approximation of reality.
Glossary
Solid The state in which a substance has a definite shape and volume at a constant
temperature.
Liquid The state in which a substance has a constant volume at a constant temperature
but can change its shape.
Gas The state in which a substance can easily change shape and volume.
Evaporation or vaporization The conversion of a liquid to a gas.
Element A substance that cannot be chemically converted into simpler substances; a
substance in which all of the atoms have the same number of protons and therefore
the same chemical characteristics.
Group All the elements in a given column on the periodic table; also called a family.
Family All the elements in a given column on the periodic table; also called a group.
Metals The elements that (1) have a metallic luster, (2) conduct heat and electric
currents well, and (3) are malleable.
Malleable Capable of being extended or shaped by the blows of a hammer.
Nonmetals The elements that do not have the characteristics of metals. Some of the
nonmetals are gases at room temperature and pressure, some are solids, and one is
a liquid. Various colors and textures occur among the nonmetals.
Metalloids or semimetals The elements that have some but not all of the characteristics
of metals.
Representative elements The elements in groups 1, 2, and 13 through 18 (the “A”
groups) on the periodic table; also called main‑group elements.
Main-group elements
The elements in groups 1, 2, and 13 through 18 (the “A”
groups) on the periodic table; also called representative elements.
Transition metals The elements in groups 3 through 12 (the “B” groups) on the
periodic table.
Inner transition elements The 28 elements at the bottom of the periodic table.
Periods The horizontal rows on the periodic table.
Atom The smallest part of an element that retains the chemical characteristics of the
element.
Atomic mass unit (u or amu) Unit of measurement for the masses of particles; 1/12
the mass of a carbon atom that has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
Proton A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron A negatively charged particle found outside the nucleus of an atom.
Neutron An uncharged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Nucleus The extremely small, positively charged core of the atom.
Ion Any charged particle, whether positively or negatively charged.
Cation An ion formed from an atom that has lost one or more electrons and thus has
become positively charged.
Anion An ion formed from an atom that has gained one or more electrons and thus
has become negatively charged.
Isotopes
Atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of
neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35