Extraction Of Metals Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
4/26/2010
Extracting Iron in Industries
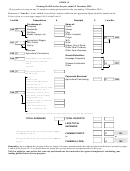
A Blast Furnace
Haematite,
coke
(which is mainly carbon),
limestone
(calcium carbonate)
are added at the
top
of the blast
furnace.
Blasts of
hot air
are
blown into the furnace
near the bottom.
slag
molten iron
Chemical Reactions that Take Place
Chemical Reactions that Take Place
in a Blast Furnace
in a Blast Furnace
1. Carbon dioxide is produced.
2. Carbon monoxide is produced.
Carbon in coke burns in hot air to
As carbon dioxide rises up in the blast
produce carbon dioxide.
furnace, it reacts with more coke to form
carbon monoxide.
C + O
CO
2
2
Limestone decomposed by heat to form
C + CO
2CO
2
carbon dioxide
and
calcium
oxide.
CaCO
CaO + CO
3
2
Chemical Reactions that Take Place
Chemical Reactions that Take Place
in a Blast Furnace
in a Blast Furnace
3. Haematite is reduced to iron.
4. Impurities are removed.
Impurities such as silicon(IV) oxide are
Carbon monoxide reduces iron(III) oxide
removed by calcium oxide.
in haematite to iron.
CaO + SiO
CaSiO
Fe
O
+ 3CO
2Fe + 3CO
2
3
2
3
2
Molten iron is formed and it runs to the bottom of the blast
CaSiO
is called
calcium silicate
or slag. It
floats
on top of
furnace.
3
molten iron. It is tapped off separately from the iron.
Waste gases
e.g. nitrogen, carbon dioxide escape from the
top
of the blast furnace.
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4