Structure Of Proteins And Chemical Bonding Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Structure and biological functions of proteins
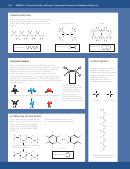
Fig 3. Three dimensional forms of polypeptide and protein molecules - Tertiary and Quaternary
Tertiary structure - (ribonuclease enzyme)
Quaternary structure - (collagen)
secondary structure
folded to form
globular coil
three parallel alpha-helices
cross bonded together into
a fibrous protein
cross sulphur bonds (give
ribonuclease stability in
o
temperatures up to 90
C
hydrogen/ionic
cross bonds
Fig 4 shows the structural formula of an alpha-helix.
Fig 4. Structural forms of an alpha-helix
sulphur bond
amino acid chain
hydrogen bond
S
R
R
S
R
H
C
C
R
H
C
O
N
C
R
O
C N
O
N
R
C
N
C
C
O
O
C
C
H
C
N
N
H
O
N
C
H
C
O
C
C
N
C
O
O
N
C
C
R
C
H
O
O
C
N
C
N
R
N
C
O
O
H
R
N
N
C
C
C
H
H
R
R
C
O
O
H
N
C
R
C
C
C
R
H
S
S
R
R
peptide bond holding adjacent
amino acids together
_
Types of protein
1. R.COOH
R.COO
+ H
+
and
2. R.NH
+ H
+
R.NH
+
2
3
In addition to being classed as fibrous or globular forms according to their
Thus, in a high hydrogen ion concentration (acid pH) reaction 1 will tend
3D structure, proteins may be classed as simple or conjugated. Simple
to be pushed to the left and reaction 2 will tend to be pushed to the right.
proteins only contain amino acids in their structure and exist as several
The amino acids will therefore be predominately positively charged cations.
different types, such as albumins, globulins and scleroproteins. Examples
of these types will be named later. Conjugated proteins contain amino acids
In a lower hydrogen ion concentration (less acid or alkaline pH) reaction 1
plus some other type of chemical molecule, such as nucleic acids in
will tend to proceed to the right and reaction 2 will tend to proceed to the
nucleoproteins, phosphoric acid in phosphoproteins and lipids in
left. The amino acids will therefore be predominantly negatively charged
lipoproteins. Haemoglobin is a conjugated protein consisting of four globular
anions.
polypeptides each of which contains a porphyrin ring which also contains iron.
There is an intermediate hydrogen ion concentration where the forward
The effect of pH on amino acids and proteins
and backward rates of reactions 1 and 2 are equal (50:50). The amino acids
The pH measures the hydrogen ion concentration of the medium in which
will then carry 50% of amine groups charged and 50% of amine groups
the amino acid or protein is, whether, for example, in blood, tissue fluid,
uncharged, 50% of acid groups charged and 50% of acid groups uncharged.
cell, animal or plant or soil. The hydrogen ion concentration will affect how
Such ions are called zwitterions (German for ‘ions of two types). The pH
the amino acids and proteins ionise. The acid and amine groups of amino
at which this occurs is a physical constant for each specific amino acid or
acids ionise as shown in the equilibrium reactions:
protein and is called the iso-electric point (IEP).
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4