Structure Of Proteins And Chemical Bonding Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Structure and biological functions of proteins
• • • • • enzymes: syllabus examples are hydrolases such as amylases, proteases
Remember – the iso-electric point is the pH at which the amino acids or
and lipases used in digestion, oxido-reductases such as the
protein carry no net charge/carry equal amounts of negative and positive
dehydrogenases used in the metabolic cycles and ligases which enable
charges.
molecules to be bonded together using the energy from ATP.
• • • • • hormones: some hormones are protein in nature, such as somatotropin
Exam hint – a common omission when defining ‘iso-electric point’ is
– pituitary growth hormone and insulin which regulates blood glucose
to fail to refer to pH . Candidates often just say ‘the iso- electric point
concentrations.
is the point at which the protein carries no net charge’. Candidates
also often incorrectly say that the IEP must be pH 7.
• • • • • contractile proteins: some proteins can contract and lengthen and thus
enable movement. Examples are actin and myosin found in muscles and
dynein making up the structure of cilia and flagella.
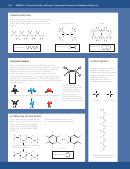
Proteins behave in a similar way to amino acids but the charges are on acid,
amine and hydroxide groups in the amino acid side chains – the core amine
• • • • • storage proteins: because of their toxic amine groups, amino acids
and acid groups are bound up in the peptide bonding. The ionic state of
cannot be stored, unless they are bound within protein structure.
amino acids is shown in Fig 5.
Examples are ovalbumin or egg white protein, casein and lactalbumins
which are milk proteins, glutelins and gliadins which are cereal seed
Fig 5. Ionic states of an amino acid
proteins and ferritin which binds up iron and stores it in the spleen,
liver and red bone marrow.
R
R
R
• • • • • transport proteins: bind on to and release insoluble or inadequately
H
H
H
soluble substances so that they can be transported through the body.
+
+
NH
NH
NH
C
C
C
3
3
2
Examples are haemoglobin for oxygen transport in vertebrate blood,
myoglobin for oxygen transport in muscles, plasma albumin which
_
_
COOH
COO
COO
transports fatty acids in blood, transferritin which transports iron
through blood to the iron storage sites and binding globulins which
cation
zwitterion
anion
transport insoluble thyroid hormones through blood.
• • • • • protective proteins; examples are the blood clotting factors such as
The charges on a protein resulting from the pH effect may have an influence
thrombin and fibrinogen which reduce bleeding during injury, antibodies
on its behaviour:
(gamma globulins) which can react with foreign proteins (antigens) to
• the charges on the active sites of an enzyme may affect the capability of
neutralise them, thus giving protection against disease, and complement
the enzyme to join with its specific substrate. This is why enzymes tend
which can form complexes with antigen-antibody systems enhancing
to work best at specific pHs.
their activity.
• at the IEP the protein carries equal numbers of opposite charges. Opposite
charges attract which may make the protein molecules clump together
• • • • • buffers: many amino acids and proteins have buffering ability and thus
and precipitate. At other pHs the protein only carries like charges.
reduce pH change within the organism. A classic example is haemoglobin
These repel molecules from each other and thus may increase the solubility.
which can react with hydrogen ions forming reduced haemoglobin.
• at extremes of pH the protein molecules may carry huge numbers of like
This buffers the blood between pH 7.2 and 7.6.
charges as reactions 1 and 2 go almost to completion. These charges may
exert a large repulsive force which breaks apart the hydrogen and ionic
• • • • • osmotic proteins: plasma albumin in blood is responsible for much of
bonds holding the 3D structure together. The 3D structure therefore
the osmotic pressure or water potential of blood, which tends to hold
breaks apart and the protein is denatured since its structure and functional
water in the blood plasma thus maintaining the blood volume. Proteins
ability is lost
in most biological fluids, such as cell sap in plant cells and in invertebrate
bloods, have a similar role.
Remember – denaturation is the loss of function of a protein caused by
• • • • • toxins; some proteins act as toxins or poisons. Examples are the
a loss of structure. Another agent of denaturation may be heat. This can
phospholipase enzymes found in many snake venoms – these destroy
disrupt the hydrogen and ionic bonds thus causing the 3D structure to
cell membranes. Many bacteria such as Clostridium tetani,
o
unravel. Most proteins denature around 45
C. Sulphur bonds are more
Clostridium botulinum and Diphtheria, release toxic chemicals that
stable to heat and thus proteins with many such bonds can withstand
are very dangerous to humans. Ricin is a toxic chemical that is found in
higher temperatures. e.g. enzymes in bacteria which live in hot springs
castor oil beans which if taken, in contaminated castor oil, causes jaundice,
and ribonuclease in saliva.
gastrointestinal problems and heart failure.
The range of biological functions of proteins
Exam hint – questions on functions of protein may often require
• • • • • structural proteins: Many structural proteins belong to the class of
continuous prose or essay type answers. Make sure that you can
scleroproteins. Examples are;
illustrate your answers by reference to specific examples for each
• • • • • collagen – found as strong non-elastic white fibres in tendons, cartilage
function.
and bone.
• • • • • elastin – found as yellow elastic fibres in ligaments and joint capsules.
• • • • • keratin – found as a horny impermeable protein in skin, hair, feathers,
nails and hooves.
Other structural proteins are the lipoproteins of cell membranes, viral
coat proteins, fibroin found as spider silk and cocoon silk, sclerotin
found in insect exoskeletons, and mucoproteins found in lubricating
joint (synovial) fluid.
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4