Chemistry Reference Sheet Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
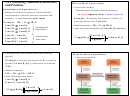
Example:
Calculate the mass of oxygen needed to
Reaction Yield
completely burn 5.4 kg of butane (C
H
).
4
10
• Theoretical yield -
the maximum amount of
→ balanced equation:
product that can be expected from a given
→ 8CO
2C
H
+ 13O
+ 10H
O
4
10
2
2
2
amount of reactant
[13 mol O
/2 mol C
H
]
→ mole ratio:
• Actual yield -
2
4
10
the actual amount of product
→ molar masses:
isolated in a reaction
→ 58.1 g/mol
→ 32.0 g/mol
C
H
O
Actual Yield ≤ Theoretical Yield
4
10
2
3
10
g
C
H
1
mol
C
H
• Percentage yield :
×
×
×
4
10
4
10
5
.
4
kg
C
H
4
10
1
kg
C
H
58
.
1
g
C
H
4
10
4
10
Actual Yield
×
% Yield =
100%
13
mol
O
32
.
0
g
O
×
=
×
4
=
2
2
1
.
9
10
g
O
19
kg
O
Theoretical Yield
2
2
2
mol
C
H
1
mol
O
4
10
2
Example:
Calculate the theoretical yield of
• Reasons for the difference between actual
carbon dioxide produced by the combustion of
and theoretical yield
25.0 g propane (C
H
) in excess oxygen.
– incomplete reaction
3
8
→balanced equation:
– loss of product
→ 3CO
C
H
+ 5O
+ 4H
O
– side reactions
3
8
2
2
2
→mass-to-mass conversion:
1 mol C H
3 mol CO
×
×
×
3
8
25.0 g C H
2
3
8
44.09 g C H
1 mol C H
3
8
3
8
44.01 g CO
×
=
→
2
74.9 g CO
Theor Yield
.
2
1 mol CO
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4