Aqueous Solutions Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Aqueous Solutions
Dissociation separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves.
In this book assume 100% dissociation for all soluble ionic compounds.
Dissociation of NaCl:
H
O
2
+
NaCl(s) à Na
(aq) + Cl
(aq)
1 mol 1 mol 1 mol
+
The solution that contains 1 mol of NaCl contains 1 mol of Na
and 1 mol of Cl
.
EX) Write the equation for the dissolution of aluminum sulfate, Al
(SO
)
, in water. How many
2
4
3
mols of aluminum ions and sulfate ions are produced by dissolving 1 mol of aluminum sulfate?
What is the total number of moles of ions produced by dissolving 1 mol of aluminum sulfate?
O
H
2
3+
2
(SO
)
(s) à 2Al
(aq) + 3SO
(aq)
Al
4
2
4
3
How many mols of aluminum ions and sulfate ions are produced by dissolving 1 mol of
aluminum sulfate?
2 mols of aluminum
3 mols of sulfate
What is the total number of moles of ions produced by dissolving 1 mol of aluminum sulfate?
2 + 3 = 5
Practice bottom of page 436.
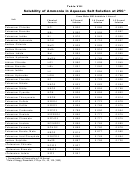
No ionic compound is completely insoluble but ones of low solubility are considered insoluble.
To determine solubility read table below.
General Solubility Guidelines
1.
Sodium, potassium, and ammonium compounds are soluble in water.
Nitrates, acetates, and chlorates are soluble.
2.
3.
Most chlorides are soluble, except those of silver, mercury(I), and lead. Lead (II) chloride
is soluble in hot water.
Most sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, lead, calcium, and mercury.
4.
5.
Most carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are insoluble, except those of sodium,
potassium, and ammonium.
Most sulfides are insoluble, except those of calcium, strontium, sodium, potassium, and
6.
ammonium.
EX) Is calcium phosphate soluble or insoluble?
Dissociation equations cannot be written for insoluble compounds.
2 compounds react à insoluble compound will be a precipitation reaction.
Precipitation occurs when attraction between the ions is greater than the attraction between the
ions and surrounding water molecules.
EX) Will a precipitate form when solutions of ammonium sulfide and cadmium nitrate are
combined?
Dissociation equations:
H
O
2
2
+
(aq) + S
(aq)
S(s) à 2NH
)
(NH
4
2
4
O
H
2
2+
(aq)
(s) à Cd
(aq) + 2NO
)
Cd(NO
3
2
3
Put these together to form:
(?) + CdS(?)
(aq) à 2NH
NO
S(aq) + Cd(NO
)
(NH
)
4
3
3
2
4
2
–look at solubility rules: is soluble
NH
NO
4
3
CdS – insoluble in aqueous solutions, so will precipitate out
SO:
(aq) + CdS(s)
NO
(aq) à 2NH
)
)
S(aq) + Cd(NO
3
(NH
4
3
2
2
4
Net Ionic Equations : includes only those compounds and ions that undergo a chemical change
in a reaction in an aqueous solution.
Convert chemical equation
NO
(aq) + CdS(s)
(aq) à 2NH
S(aq) + Cd(NO
)
3
)
4
(NH
2
3
4
2
To the overall ionic equation:
+
(aq)
(aq) + 2NH
+
2
(aq) à CdS(s) +2NO
2+
(aq) + S
4
(aq) + 2NH
3
(aq) + 2NO
Cd
4
3
Spectator ions : ions that do not take part in a chemical reaction and are found in solution both
before and after the reaction.
To make it a net ionic equation, the spectator ions are cancelled on both sides of the equation.
Net ionic equation:
2
2+
(aq) à CdS(s)
(aq) + S
Cd
EX) Identify the precipitate that forms when aqueous solutions of zinc nitrate and ammonium
sulfide are combined. Write the equation for the possible doubledisplacement reaction. Then
write the formula equation, overall ionic equation, and net ionic equation for the reaction.
Sep 192:17 PM
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2