Protein Synthesis Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
SICM Tuition
Biology AS
In the cytoplasm
-
the spliced mRNA then moves out of the nucleus via a nuclear pore
-
the mRNA goes to a ribosome
-
the first triplet code to be read is AUG. This codes for the start codon
(methionine)
-
the codes on the mRNA are called codons
-
the ribosome can hold 2 triplet codes together…
-
the mRNA enters the ribosome and as it does so, tRNA (transfer RNA) comes
and joins complementary bases to it. The complementary triplet bases on the tRNA
are called anti-codons.
-
a tRNA molecule is made up of three bases at one end and an amino acid at the
other end
-
many different tRNA molecules are present in the cytoplasm for this to occur
-
this continues and as it does, the amino acids line up (2 at a time – as each
ribosome can hold 2 triple codes) and bond together by peptide bonds catalysed
by the enzyme peptidyl transferase.
-
This continues until a stop codon is reached. The stop codons do not code for any
amino acid, but stop the translation.
-
many amino acids make up a protein
-
the mRNA that moves along can simply be re-used again and again
Translation animation
Highly recommended….very nice way to put it all together
Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2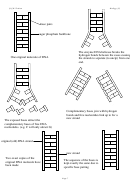 3
3 4
4