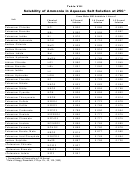
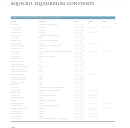
Aqueous Solutions Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
+
-
NaCl
Na
+ Cl
(s)
(aq)
(aq)
Ex. dissolving magnesium fluoride
2+
-
MgF
Mg
+ 2 F
2 (s)
(aq)
(aq)
NOTE: ions are present in solution solution will be able to conduct electricity
Most bases are ionic compounds that contain the OH
-
-
ion. When bases dissociate, the OH
ion is responsible for the properties of bases (eg. turning litmus paper blue)
Ex.
2+
-
Ba(OH)
Ba
+ 2 OH
2 (s)
(aq)
(aq)
Most acids are molecular compounds only neutral molecules are present. However, when
acids dissolve in water, they become electrolytes.
Acids separate into individual molecules and ionize into positive hydrogen ions and negative
anions.
Ionization is the reaction of neutral atoms or molecules to form charged ions.
Ex.
+
-
HCl
H
+ Cl
(g)
(aq)
(aq)
Acids can be classified as strong or weak.
Strong acids will completely ionize in solution. They are very good electrical conductors.
Strong acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrochloric acid.
Weak acids will only partially ionize in solution. They will not conduct electricity as well as
strong acids.
Common weak acids include:
Acetic acid -- CH
COOH
3
Citric acid -- H
C
H
O
3
6
5
7
Benzoic acid -- C
H
COOH
6
5
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4