Elements And Isotopes Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
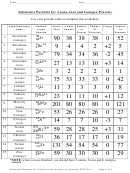
Chemical
Atomic
Atomic
Chemical Name
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Symbol
number
mass
Boron
B
5
5
6
5
11
Sodium
Na
11
11
13
11
24
Gallium
Ga
31
31
37
31
68
Yttrium
Y
39
39
50
39
89
Copper
Cu
29
29
35
29
64
Technetium
Tc
43
43
57
43
100
Pb
Lead
82
82
125
82
207
Ytterbium
Yb
70
70
102
70
172
Actinium
Ac
89
89
136
89
225
Molybdenum
Mo
42
42
53
42
95
Thallium
Tl
81
81
125
81
206
Fermium
Fm
100
100
159
100
259
Nobelium
No
102
102
159
102
261
Ytterbium
Yb
70
70
102
70
172
Seaborgium
Sg
106
106
159
106
265
2.2
Properties of Water
The Water Molecule
Water molecules (H
O) are polar because of an uneven distribution of electrons, creating a slight negative
2
(–) charge in the oxygen atom and a slight positive (+) charge in each hydrogen atom. The attraction between a hydrogen atom of
one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule is called a hydrogen bond.
Cohesion is an
attraction between molecules of the same substance. It causes water molecules to be drawn together,
producing surface tension
Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. It causes capillary action, an effect that causes water to
rise in a narrow tube against the force of gravity.
Solutions and Suspensions
A mixture is a material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed
together but not chemically combined. A solution is a mixture in which all the components are evenly spread out: the substance
dissolved is the solute; the substance that causes the dissolving is the solvent. Mixtures of water and undissolved materials are
suspensions.
–
+
Acids, Bases, and pH
A water molecule (H
O) can split apart to form a hydrogen ion (H
) and a hydroxide ion (OH
).
2
The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The scale ranges from 0 to 14. Pure water has a pH
of
7.
+
An acid is any compound that forms H
ions in solution. Acidic solutions have pH values below 7. A base is a compound that
–
forms OH
ions in solution. Basic, or alkaline, solutions have pH values above 7.
Buffers are weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden changes in pH.
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4