Grade 5 Staar Assessed Curriculum
ADVERTISEMENT
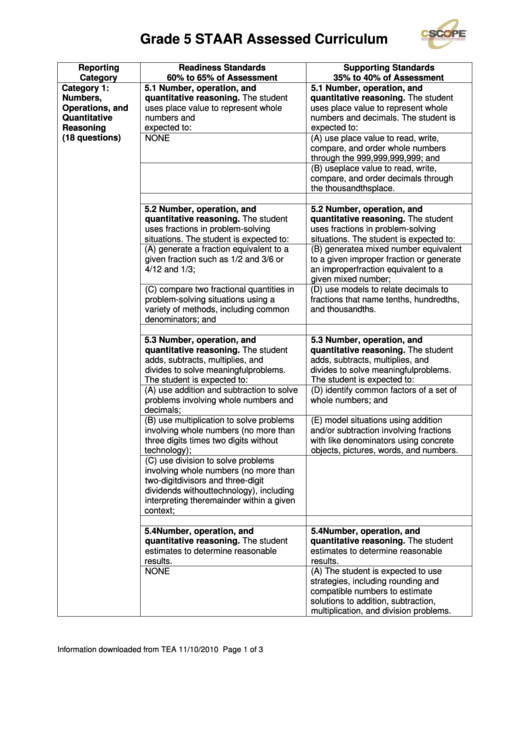
Grade 5 STAAR Assessed Curriculum
Reporting
Readiness Standards
Supporting Standards
Category
60% to 65% of Assessment
35% to 40% of Assessment
Category 1:
5.1 Number, operation, and
5.1 Number, operation, and
Numbers,
quantitative reasoning. The student
quantitative reasoning. The student
Operations, and
uses place value to represent whole
uses place value to represent whole
Quantitative
numbers and decimals. The student is
numbers and decimals. The student is
Reasoning
expected to:
expected to:
(18 questions)
NONE
(A) use place value to read, write,
compare, and order whole numbers
through the 999,999,999,999; and
(B) use place value to read, write,
compare, and order decimals through
the thousandths place.
5.2 Number, operation, and
5.2 Number, operation, and
quantitative reasoning. The student
quantitative reasoning. The student
uses fractions in problem-solving
uses fractions in problem-solving
situations. The student is expected to:
situations. The student is expected to:
(A) generate a fraction equivalent to a
(B) generate a mixed number equivalent
given fraction such as 1/2 and 3/6 or
to a given improper fraction or generate
4/12 and 1/3;
an improper fraction equivalent to a
given mixed number;
(C) compare two fractional quantities in
(D) use models to relate decimals to
problem-solving situations using a
fractions that name tenths, hundredths,
variety of methods, including common
and thousandths.
denominators; and
5.3 Number, operation, and
5.3 Number, operation, and
quantitative reasoning. The student
quantitative reasoning. The student
adds, subtracts, multiplies, and
adds, subtracts, multiplies, and
divides to solve meaningful problems.
divides to solve meaningful problems.
The student is expected to:
The student is expected to:
(A) use addition and subtraction to solve
(D) identify common factors of a set of
problems involving whole numbers and
whole numbers; and
decimals;
(B) use multiplication to solve problems
(E) model situations using addition
involving whole numbers (no more than
and/or subtraction involving fractions
three digits times two digits without
with like denominators using concrete
technology);
objects, pictures, words, and numbers.
(C) use division to solve problems
involving whole numbers (no more than
two-digit divisors and three-digit
dividends without technology), including
interpreting the remainder within a given
context;
5.4 Number, operation, and
5.4 Number, operation, and
quantitative reasoning. The student
quantitative reasoning. The student
estimates to determine reasonable
estimates to determine reasonable
results.
results.
NONE
(A) The student is expected to use
strategies, including rounding and
compatible numbers to estimate
solutions to addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and division problems.
Information downloaded from TEA 11/10/2010
Page 1 of 3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3








