Proteins Structure Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s
c) The diagram (modified from the Chemguide page) shows a close-up view of one of these
ribbons. Mark the intermolecular forces on the diagram.
This diagram (also modified from the Chemguide page)
shows some of the bits of the protein chain in the spirals.
d) What name is given to the spirals?
e) Name the intermolecular forces holding the spiral
together and mark them on the diagram.
f) What is represented by the string-like sections of the
protein?
g) Proteins are described in terms of their primary,
secondary and tertiary structures (and quaternary, but we
aren’t concerned with that at this level). What level of structure are we talking about in the
diagrams above?
3. The overall shape of a protein, the tertiary structure (if you said that in the last question, you were
wrong!), is controlled by ionic interactions, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals dispersion forces and
sulphur-sulphur bridges between the chains. Explain how each of these arises. (Be as precise as
you can, but you are not expected to be able to name specific amino acids, or know the structures of
specific side-groups.)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1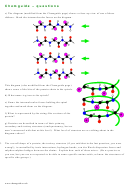 2
2








