Project Implementation Plan Page 18
ADVERTISEMENT
Page 18 of 20
FM0027-GDL-00034-E-V15
5. Estimate activity cost
Based on the identified resources and the activity duration, an estimate for the activity’s cost can be
made. If the cost is unacceptable, consider modifying the resource level and thus the activity duration
6. Define activity sequence
The list of activities defined by the WBS need to be ordered before a project schedule can be
developed. Some activities can be performed in parallel; some activities have interdependencies that
mean they have to be performed in series.
The most common way of defining an activity sequence is by means of a network diagram.
Figure 7: example network diagram (project tasks represented by nodes)
7. Create project schedule and budget
A project schedule is created by calculating the overall duration of the project based on the sequence
of the activities, and thus defining planned start and end dates for each activity. The critical path
method is commonly used for this purpose.
Figure 8: example network diagram showing possible critical path between activities
It may be that resource or other constraints mean that activities that could logically be performed in
parallel have to be serialised – in this case it will be necessary to modify the activity sequence to reflect
such constraints.
With the planned start and finish dates of each activity defined by the schedule, a project budget can
be established, detailing the expenditure over the time of the project’s execution.
Financial Mechanism Office, 12/16, Rue Joseph II, 1000 Brussels, Belgium . Tel: +32 (0)2 286 1701 . Fax: +32 (0)2 286 1789 . Email: fmo@efta.int .
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17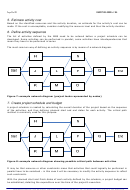 18
18 19
19 20
20








