Mitosis, Meiosis, And Patterns Of Inheritance Worksheet Page 26
ADVERTISEMENT
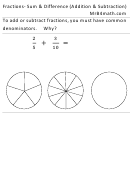
39.
In chickens, a sex-linked dominant allele causes a feather pattern known as “barred”. If a barred hen is
mated with a non-barred rooster, what will be the feather pattern and sex of the offspring?
IIX. Dominant Genetic Diseases (text p. 181 - Huntington’s Disease)
Some genetic disorders and traits are the result of expression of one or more dominant alleles. An example of
dominant diseases or disorders include Huntington’s Disease and polydactyly. Huntington’s disease is a fatal
genetic disorder that results in the deterioration of the brain and nervous system later in life. Usually
individuals with Huntington’s disease have only one copy of the dominant allele. The most unfortunate aspect
of Huntington’s disease is the person who has the dominant allele passes the allele to their children before the
parent’s symptoms of the disorder are present.
A person with Huntington’s disease has the following genotype: _______ and shape in pedigree is: _________
A person without Huntington’s disease has the following genotype: _______ and shape in pedigree is: _______
40. Determine the genotypes for every member of the family:
41. Polydactyly a condition in which a person has an extra finger or toes on one or both hands or feet. A
mother with polydactyly marries a man without polydactyly. If the couple has 20 children, how many
children would you expect to have polydactyly?
26
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15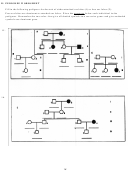 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21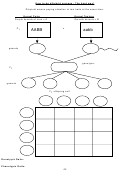 22
22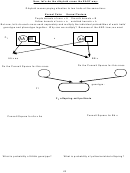 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27