Gcc Chm152ll: Nuclear Chemistry - Radioactivity, Decay, Dating, And Other Hazards Worksheets Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
c. How much of a 675 mg sample of Bismuth-210 would remain after 20.04 days?
d. What is the value of the rate constant, k, for Bismuth-210? Include units for k!
e. How much of a 146 mg sample of Bismuth-210 would remain after 32.1 days?
f. How much time would it take for 415 mg of Bismuth-210 to decay to 125 mg?
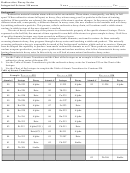
III. Applications of Radioactive Isotopes
The half-lives of different radioactive nuclides range from fractions of a second to billions of years.
Examples of parent-daughter pairs, their decay processes, half-lives, and applications are listed in the table
below.
Table 2: Half-lives, Types of Decay and Applications of Radioactive Isotopes
Parent/Daughter
Decay Process
Half-life
Application
Industrial applications and treatment
Strontium-90 / Yttrium-90
ß emission
28.8 years
for eye and skin diseases
–
e
capture and
Iodine-123 / Tellerium-123
13 hours
Thyroid imaging
emission
Iodine-131 / Xenon-131
ß emission
8 days
Thyroid treatment
Technetium-99m (excited) /
emission
6 hours
Bone scans
Technetium-99
Leukemia Therapy; tracers used in
Phosphorus-32 / Sulfur-32
ß emission
14.28 days
DNA sequencing
Americium-241 / Neptunium-237
ß and emissions
432 years
Smoke detectors
Plutonium-239 / Uranium-235
and emissions
24,400 years
Nuclear reactors
series of and
Uranium-235 / Pb-207
713 million years
emissions
Potassium-40 /Argon-40
electron capture
1.25 billion years
Carbon-14 / Nitrogen-14
emission
5730 years
Archeological Dating
Rubidium-87 / Strontium-87
emission
50 billion years
GCC CHM152LL: Nuclear Chemistry
p.
5 of 7
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7