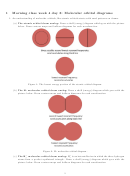
Molecular Orbital Theory, Valence Bond Theory And Hybridization Worksheets Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Chemistry 121 Problem set VI solutions - 3
F
F
Xe
F
F
-
NO
2
a) Lewis structure is first structure and and has a formal charge on one oxygen to give a net charge of -1.
Nitrogen forms one double bond and there are two resonance hybrids.
b) VSEPR
2 bp + 1 lp = 3
(multiple bonds count as one bp)
shape is trigonal.
c) Molecular shape is bent. (second structure).
2
d) Hybridization is sp
(VSEPR 3 pairs on central atom so need 3 orbitals)
e) Polar and the resultant of the two NO vectors will not cancel with the lone pair vector. Molecule has a
net negative charge.
N
O
O
O
O
2.
C
VSEPR 4 bp + 0 lp = 4 pair
tetrahedral
A
3
Hybridization
sp
(VSEPR 4 pairs on central atom so need 4 orbitals)
C
VSEPR 3 bp + 0 lp = 3 pair
trigonal planar (multiple bonds count as one bp)
B
2
Hybridization
sp
(VSEPR 3 pairs on central atom so need 3 orbitals)
3.
a) CH
CH
3
3
H
H
H
C
C
H
H
H
3
Carbon
VSEPR: 4 bp + 0 lp = 4 pairs; tetrahedral and hybridization is sp
2
3
sp
2s
Carbon
3
The six carbon-hydrogen bond orbitals in ethane result from the over lap of sp
orbitals on the carbon
atoms and 1s orbitals on the hydrogen atoms. The carbon-carbon bond orbital results from the overlap of
3
two sp
orbitals, one from each carbon atom. There are (6 x 1) + (2 x 4) = 14 valence electrons in ethane.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2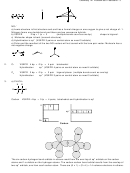 3
3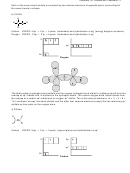 4
4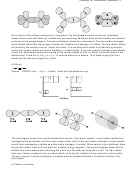 5
5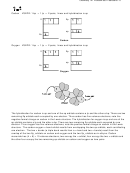 6
6 7
7 8
8